Exome sequencing in undiagnosed inherited and sporadic ataxias
- PMID: 25497598
- PMCID: PMC4306819
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awu348
Exome sequencing in undiagnosed inherited and sporadic ataxias
Abstract
Inherited ataxias are clinically and genetically heterogeneous, and a molecular diagnosis is not possible in most patients. Having excluded common sporadic, inherited and metabolic causes, we used an unbiased whole exome sequencing approach in 35 affected individuals, from 22 randomly selected families of white European descent. We defined the likely molecular diagnosis in 14 of 22 families (64%). This revealed de novo dominant mutations, validated disease genes previously described in isolated families, and broadened the clinical phenotype of known disease genes. The diagnostic yield was the same in both young and older-onset patients, including sporadic cases. We have demonstrated the impact of exome sequencing in a group of patients notoriously difficult to diagnose genetically. This has important implications for genetic counselling and diagnostic service provision.
Keywords: ataxia; whole exome sequencing.
© The Author (2014). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Figures
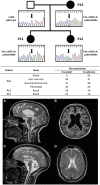
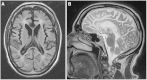
Comment in
-
Evaluation of exome sequencing variation in undiagnosed ataxias.Brain. 2015 Oct;138(Pt 10):e383. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv087. Epub 2015 Apr 4. Brain. 2015. PMID: 25842391 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply: Evaluation of exome sequencing variation in undiagnosed ataxias.Brain. 2015 Oct;138(Pt 10):e384. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv088. Epub 2015 Apr 4. Brain. 2015. PMID: 25842392 No abstract available.
References
-
- Anheim M, Fleury M, Monga B, Laugel V, Chaigne D, Rodier G, et al. Epidemiological, clinical, paraclinical and molecular study of a cohort of 102 patients affected with autosomal recessive progressive cerebellar ataxia from Alsace, Eastern France: implications for clinical management. Neurogenetics. 2010;11:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Bamshad MJ, Ng SB, Bigham AW, Tabor HK, Emond MJ, Nickerson DA, et al. Exome sequencing as a tool for Mendelian disease gene discovery. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12:745–55. - PubMed
-
- Carstea ED, Morris JA, Coleman KG, Loftus SK, Zhang D, Cummings C, et al. Niemann-Pick C1 disease gene: homology to mediators of cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1997;277:228–31. - PubMed
-
- Casari G, De Fusco M, Ciarmatori S, Zeviani M, Mora M, Fernandez P, et al. Spastic paraplegia and OXPHOS impairment caused by mutations in paraplegin, a nuclear-encoded mitochondrial metalloprotease. Cell. 1998;93:973–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

