Claudin-7 expression induces mesenchymal to epithelial transformation (MET) to inhibit colon tumorigenesis
- PMID: 25500541
- PMCID: PMC4804637
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2014.385
Claudin-7 expression induces mesenchymal to epithelial transformation (MET) to inhibit colon tumorigenesis
Abstract
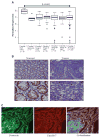
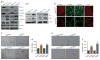
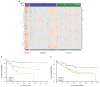
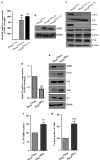
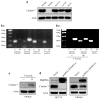
In normal colon, claudin-7 is one of the highly expressed claudin proteins and its knockdown in mice results in altered epithelial cell homeostasis and neonatal death. Notably, dysregulation of the epithelial homeostasis potentiates oncogenic transformation and growth. However, the role of claudin-7 in the regulation of colon tumorigenesis remains poorly understood. Using a large colorectal cancer (CRC) patient database and mouse models of colon cancer, we found claudin-7 expression to be significantly downregulated in cancer samples. Most notably, forced claudin-7 expression in poorly differentiated and highly metastatic SW620 colon cancer cells induced epithelial characteristics and inhibited their growth in soft agar and tumor growth in vivo. By contrast, knockdown of claudin-7 in HT-29 or DLD-1 cells induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), colony formation, xenograft-tumor growth in athymic mice and invasion. Importantly, a claudin-7 signature gene profile generated by overlapping the DEGs (differentially expressed genes in a high-throughput transcriptome analysis using claudin-7-manipulated cells) with human claudin-7 signature genes identified high-risk CRC patients. Furthermore, Rab25, a colon cancer suppressor and regulator of the polarized cell trafficking constituted one of the highly upregulated DEGs in claudin-7 overexpressing cells. Notably, silencing of Rab25 expression counteracted the effects of claudin-7 expression and not only increased proliferation and cell invasion but also increased the expression of p-Src and mitogen-activated protein kinase-extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 that were suppressed upon claudin-7 overexpression. Of interest, CRC cell lines, which exhibited decreased claudin-7 expression, also exhibited promoter DNA hypermethylation, a modification associated with transcriptional silencing. Taken together, our data demonstrate a previously undescribed role of claudin-7 as a colon cancer suppressor and suggest that loss of claudin-7 potentiates EMT to promote colon cancer, in a manner dependent on Rab25.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Tsukita S, Furuse M, Itoh M. Multifunctional strands in tight junctions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:285–293. - PubMed
-
- Schneeberger EE, Lynch RD. The tight junction: a multifunctional complex. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004;286:C1213–C1228. - PubMed
-
- Soler AP, Miller RD, Laughlin KV, Carp NZ, Klurfeld DM, Mullin JM. Increased tight junctional permeability is associated with the development of colon cancer. Carcinogenesis. 1999;20:1425–1431. - PubMed
-
- Turksen K, Troy TC. Barriers built on claudins. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:2435–2447. - PubMed
-
- Sheehan GM, Kallakury BV, Sheehan CE, Fisher HA, Kaufman RP, Jr, Ross JS. Loss of claudins-1 and -7 and expression of claudins-3 and -4 correlate with prognostic variables in prostatic adenocarcinomas. Hum Pathol. 2007;38:564–5692007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA069457/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R25 GM062459/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA095103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA124977/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA095103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA124977/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK058404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA158472/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK088902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA158472/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK088902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA68485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA069457/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK058404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX002086/BX/BLRD VA/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

