Serum gamma - glutamyltransferase is associated with albuminuria: a population-based study
- PMID: 25500578
- PMCID: PMC4263709
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114970
Serum gamma - glutamyltransferase is associated with albuminuria: a population-based study
Abstract
Background: Serum γ - glutamyltransferase (GGT) is implicated in the pathogenesis of endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Albuminuria is a marker of endothelial damage and correlated with structural and functional integrity of the vasculature. Our objective was to evaluate the association between serum GGT level and prevalence of albuminuria in a Chinese population.
Materials and methods: We conducted a population-based cross-sectional study in 9,702 subjects aged 40 years or older. Increased urinary albumin excretion was defined according to the urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR) ranges greater or equal than 30 mg/g. Low-grade albuminuria was defined according to the highest quartile of ACR in participants without increased urinary albumin excretion.
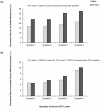
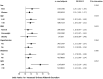
Results: The prevalence of low-grade albuminuria and increased urinary albumin excretion were respectively 23.4% and 6.6% in this population and gradually increased across the sex-specific serum GGT quartiles (all P for trend <0.05). In logistic regression analysis, compared with subjects in the lowest quartile of serum GGT level, the adjusted odds ratios (ORs) in the highest quartile was 1.22 [95% confidence interval (CI), 1.04-1.43] for low-grade albuminuria and 1.55 (95% CI, 1.18-2.04) for increased urinary albumin excretion. In subgroup analysis, significant relationship of serum GGT level with both low-grade albuminuria and increased urinary albumin excretion were detected in women, younger subjects, overweight subjects and in those with hypertension or glomerular filtration rate greater than 90 (all P <0.05).
Conclusion: Serum GGT level is associated with urinary albumin excretion in middle-aged and elderly Chinese.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Whitfield JB (2001) Gamma glutamyl transferase. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 38:263–355. - PubMed
-
- Drozdz R, Parmentier C, Hachad H, Leroy P, Siest G, et al. (1998) gamma-Glutamyltransferase dependent generation of reactive oxygen species from a glutathione/transferrin system. Free Radic Biol Med 25:786–792. - PubMed
-
- Karp DR, Shimooku K, Lipsky PE (2001) Expression of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase protects ramos B cells from oxidation-induced cell death. J Biol Chem 276:3798–3804. - PubMed
-
- Yilmaz MI, Turgut F, Kanbay M, Saglam M, Sonmez A, et al. (2013) Serum gamma-glutamyltransferase levels are inversely related to endothelial function in chronic kidney disease. Int Urol Nephrol 45:1071–1078. - PubMed
-
- Lee DS, Evans JC, Robins SJ, Wilson PW, Albano I, et al. (2007) Gamma glutamyl transferase and metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease, and mortality risk: the Framingham Heart Study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:127–133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

