Posttraumatic mucormycosis: a nationwide study in France and review of the literature
- PMID: 25500709
- PMCID: PMC4602436
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000221
Posttraumatic mucormycosis: a nationwide study in France and review of the literature
Erratum in
- Medicine (Baltimore). 2014 Nov;93(24):414
Abstract
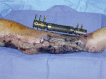
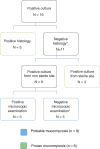
Data on clinical, mycologic characteristics, and outcome of posttraumatic mucormycosis are scarce and often limited to case reports. From the French nationwide "RetroZygo" study, we compared posttraumatic mucormycosis cases with other forms of mucormycosis. We also reviewed reports of posttraumatic mucormycosis in the English-language literature from 1993 to 2013. We included all proven or probable cases for which underlying condition, route of infection, surgical and antifungal treatments, and outcome were detailed. From our cohort, posttraumatic mucormycosis (n = 16) differed significantly from other forms (n = 85) by rarity of underlying disease (31.2% vs 81%, p < 0.0001), frequency of cutaneous localization (87% vs 7%, p < 0.0001), short time before diagnosis (4.5 vs 21 d, p = 0.0002), species involved (Apophysomyces elegans complex and Saksenaea vasiformis), surgical requirement (93.7% vs 47%, p = 0.0006) and better survival (87.5% vs 47.6% at day 90, p = 0.03). We studied 122 cases of posttraumatic mucormycosis through our literature review. Most frequently reported traumas were traffic (37%), domestic accidents (15.1%), or natural disasters (13.4%). Mucormycosis occurred after extensive soft-tissue damage in 47.5% cases, with symptoms occurring a median of 9.5 days after trauma with necrosis being reported in 76.2% cases. Dissemination was found in 9% of patients, and bacterial coinfection in 41%. Nineteen percent of cases occurred in the Middle East or in India where Apophysomyces elegans complex was the predominant species recovered. Awareness of mucormycosis as a cause of posttrauma soft-tissue infection is warranted, especially in cases of soil-contaminated wounds. Survival is higher than in other forms of mucormycosis, but morbidity remains high.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial support and conflicts of interest: The authors have no financial support to declare for this work. F.L. has received travel grants or speaker's fees from MSD and Gilead Science. O.L. has been a consultant for Gilead Sciences, and has received grants or speaker's fees from Astellas, Pfizer, Merck, and Gilead Sciences. All other authors report no potential conflicts.
Figures



References
-
- Andresen D, Donaldson A, Choo L, et al. Multifocal cutaneous mucormycosis complicating polymicrobial wound infections in a tsunami survivor from Sri Lanka. Lancet. 2005; 365:876–878. - PubMed
-
- Arnaiz-Garcia ME, Alonso-Pena D, Gonzalez-Vela M, et al. Cutaneous mucormycosis: report of five cases and review of the literature. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. JPRAS. 2009; 62:434–441. - PubMed
-
- Bitar D, Morizot G, Van Cauteren D, et al. Estimating the burden of mucormycosis infections in France (2005-2007) through a capture-recapture method on laboratory and administrative data. Rev Epidemiologie Sante Publique. 2012; 60:383–387. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

