Sitagliptin protects rat kidneys from acute ischemia-reperfusion injury via upregulation of GLP-1 and GLP-1 receptors
- PMID: 25500876
- PMCID: PMC4571325
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2014.98
Sitagliptin protects rat kidneys from acute ischemia-reperfusion injury via upregulation of GLP-1 and GLP-1 receptors
Abstract
Aim: Sitagliptin, an oral glucose-lowering agent, has been found to produce cardiovascular protection possibly via anti-inflammatory and anti-atherosclerotic activities of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1). The aim of this study was to investigate whether sitagliptin protected the kidney function from acute ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury in rats.
Methods: Adult male SD rats were categorized into 4 groups: sham control, IR injury, IR+sitagliptin (300 mg/kg) and IR+sitagliptin (600 mg/kg). Acute renal IR injury of both kidneys was induced by clamping the renal pedicles for 1 h. The drug was orally administered at 1, 24 and 48 h after acute IR. Blood samples and 24-h urine were collected before and at 72 h after acute IR. Then the rats were sacrificed, and the kidneys were harvested for biochemical and immunohistochemical studies.
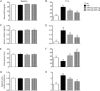
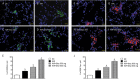
Results: Acute IR procedure markedly increased serum levels of creatinine and BUN and the ratio of urine protein to creatinine. The kidney injury score, inflammatory biomarkers (MMP-9, TNF-α and NF-κB) levels and CD68+ cells in IR kidneys were considerably increased. The expression of oxidized protein, reactive oxygen species (NOX-1, NOX-2) and apoptosis proteins (Bax, caspase-3, PARP) in IR kidneys was also significantly upregulated. All these pathological changes were suppressed by sitagliptin in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, the serum GLP-1 level, and the expression of GLP-1 receptor, anti-oxidant biomarkers (HO-1 and NQO-1 cells, as well as SOD-1, NQO-1 and HO-1 proteins), and angiogenesis markers (SDF-1α+ and CXCR4+ cells) in IR kidneys were significantly increased, and further upregulated by sitagliptin.
Conclusion: Sitagliptin dose-dependently protects rat kidneys from acute IR injury via upregulation of serum GLP-1 and GLP-1 receptor expression in kidneys.
Figures






References
-
- Coresh J, Selvin E, Stevens LA, Manzi J, Kusek JW, Eggers P, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA 2007; 298: 2038–47. - PubMed
-
- Stel VS, Kramer A, Zoccali C, Jager KJ. The 2006 ERA-EDTA Registry annual report: a precis. J Nephrol 2009; 22: 1–12. - PubMed
-
- Arogundade FA, Barsoum RS. CKD prevention in Sub-Saharan Africa: a call for governmental, nongovernmental, and community support. Am J Kidney Dis 2008; 51: 515–23. - PubMed
-
- Grassmann A, Gioberge S, Moeller S, Brown G. ESRD patients in 2004: global overview of patient numbers, treatment modalities and associated trends. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2005; 20: 2587–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

