Dynamic expression of transcription factors T-bet and GATA-3 by regulatory T cells maintains immunotolerance
- PMID: 25501630
- PMCID: PMC4297509
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.3053
Dynamic expression of transcription factors T-bet and GATA-3 by regulatory T cells maintains immunotolerance
Abstract
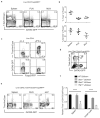
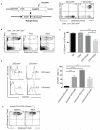
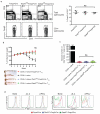
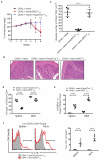
Regulatory T cells (Treg cells) can express the transcription factors T-bet and GATA-3, but the function of this expression and whether such cells represent stable subsets is still unknown. By using various reporter tools, we found that the expression of T-bet and GATA-3 in Treg cells was dynamically influenced by the cytokine environment. Treg cell-specific deletion of the gene encoding either T-bet (Tbx21) or GATA-3 (Gata3) alone did not result in loss of Treg cell function; however, mice with combined deficiency in both genes in Treg cells developed severe autoimmune-like diseases. Loss of Treg cell function correlated with upregulation of expression of the transcription factor RORγt and reduced expression of the transcription factor Foxp3. Thus, in the steady state, activated Treg cells transiently upregulated either T-bet or GATA-3 to maintain T cell homeostasis.
Figures



References
-
- Ivanov II, McKenzie BS, Zhou L, Tadokoro CE, Lepelley A, Lafaille JJ, et al. The orphan nuclear receptor RORgammat directs the differentiation program of proinflammatory IL-17+ T helper cells. Cell. 2006;126(6):1121–1133. - PubMed
-
- Hwang ES, Szabo SJ, Schwartzberg PL, Glimcher LH. T helper cell fate specified by kinase-mediated interaction of T-bet with GATA-3. Science (New York, NY. 2005;307(5708):430–433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

