Remote regulation of glucose homeostasis in mice using genetically encoded nanoparticles
- PMID: 25501906
- PMCID: PMC4894538
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.3730
Remote regulation of glucose homeostasis in mice using genetically encoded nanoparticles
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Remote regulation of glucose homeostasis in mice using genetically encoded nanoparticles.Nat Med. 2015 May;21(5):537. doi: 10.1038/nm0515-537b. Nat Med. 2015. PMID: 25951532 No abstract available.
Abstract
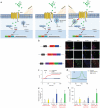
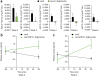
Means for temporally regulating gene expression and cellular activity are invaluable for elucidating underlying physiological processes and would have therapeutic implications. Here we report the development of a genetically encoded system for remote regulation of gene expression by low-frequency radio waves (RFs) or a magnetic field. Iron oxide nanoparticles are synthesized intracellularly as a GFP-tagged ferritin heavy and light chain fusion. The ferritin nanoparticles associate with a camelid anti-GFP-transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 fusion protein, αGFP-TRPV1, and can transduce noninvasive RF or magnetic fields into channel activation, also showing that TRPV1 can transduce a mechanical stimulus. This, in turn, initiates calcium-dependent transgene expression. In mice with stem cell or viral expression of these genetically encoded components, remote stimulation of insulin transgene expression with RF or a magnet lowers blood glucose. This robust, repeatable method for remote regulation in vivo may ultimately have applications in basic science, technology and therapeutics.
Figures



References
-
- Davidson BL, Breakefield XO. Viral vectors for gene delivery to the nervous system. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003;4:353–364. - PubMed
-
- Ando H, Furuta T, Tsien RY, Okamoto H. Photo-mediated gene activation using caged RNA/DNA in zebrafish embryos. Nat. Genet. 2001;28:317–325. - PubMed
-
- Cambridge SB, Davis RL, Minden JS. Drosophila mitotic domain boundaries as cell fate boundaries. Science. 1997;277:825–828. - PubMed
-
- Wang X, Chen X, Yang Y. Spatiotemporal control of gene expression by a light-switchable transgene system. Nat. Methods. 2012;9:266–269. - PubMed
-
- Gossen M, et al. Transcriptional activation by tetracyclines in mammalian cells. Science. 1995;268:1766–1769. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

