Low MITF/AXL ratio predicts early resistance to multiple targeted drugs in melanoma
- PMID: 25502142
- PMCID: PMC4428333
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms6712
Low MITF/AXL ratio predicts early resistance to multiple targeted drugs in melanoma
Abstract
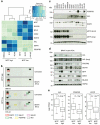
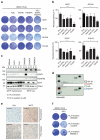
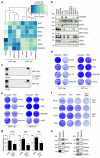
Increased expression of the Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) contributes to melanoma progression and resistance to BRAF pathway inhibition. Here we show that the lack of MITF is associated with more severe resistance to a range of inhibitors, while its presence is required for robust drug responses. Both in primary and acquired resistance, MITF levels inversely correlate with the expression of several activated receptor tyrosine kinases, most frequently AXL. The MITF-low/AXL-high/drug-resistance phenotype is common among mutant BRAF and NRAS melanoma cell lines. The dichotomous behaviour of MITF in drug response is corroborated in vemurafenib-resistant biopsies, including MITF-high and -low clones in a relapsed patient. Furthermore, drug cocktails containing AXL inhibitor enhance melanoma cell elimination by BRAF or ERK inhibition. Our results demonstrate that a low MITF/AXL ratio predicts early resistance to multiple targeted drugs, and warrant clinical validation of AXL inhibitors to combat resistance of BRAF and NRAS mutant MITF-low melanomas.
Figures
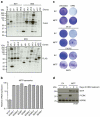
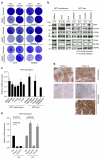
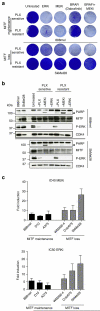
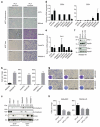

Comment in
-
The UPs and DOWNs of MITF in melanoma resistance.Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2015 Mar;28(2):132-3. doi: 10.1111/pcmr.12338. Epub 2014 Dec 23. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2015. PMID: 25476804 No abstract available.
References
-
- Davies H, et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature. 2002;417:949–954. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

