Modulation of systemic and mucosal immunity against an inactivated vaccine of Newcastle disease virus by oral co-administration of live attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium expressing chicken interleukin-18 and interferon-α
- PMID: 25502364
- PMCID: PMC4427739
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.14-0495
Modulation of systemic and mucosal immunity against an inactivated vaccine of Newcastle disease virus by oral co-administration of live attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium expressing chicken interleukin-18 and interferon-α
Abstract
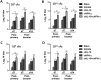
Newcastle disease (ND) is a highly contagious disease of chickens causing significant economic losses worldwide. Due to limitations in the efficacy against currently circulating ND viruses, existing vaccination strategies require improvements, and incorporating immunomodulatory cytokines with existing vaccines might be a novel approach. Here, we investigated the systemic and mucosal immunomodulatory properties of oral co-administration of chicken interleukin-18 (chIL-18) and chicken interferon-α (chIFN-α) using attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium on an inactivated ND vaccine. Our results demonstrate that oral administration of S. enterica serovar Typhimurium expressing chIL-18 or chIFN-α provided enhanced systemic and mucosal immune responses, as determined by serum hemagglutination inhibition antibody and NDV Ag-specific IgG as well as NDV Ag-specific IgA in lung and duodenal lavages of chickens immunized with inactivated ND vaccine via the intramuscular or intranasal route. Notably, combined oral administration of S. enterica serovar Typhimurium expressing chIL-18 and chIFN-α significantly enhanced systemic and mucosal immunity in ND-vaccinated chickens, compared to single administration of S. enterica serovar Typhimurium expressing chIL-18 or chIFN-α. In addition, oral co-administration of S. enterica serovar Typhimurium expressing chIL-18 and chIFN-α provided enhanced NDV Ag-specific proliferation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells and Th1-biased cell-mediated immunity, compared to single administration of either construct. Therefore, our results provide valuable insight into the modulation of systemic and mucosal immunity by incorporation of immunomodulatory chIL-18 and chIFN-α using Salmonella vaccines into existing ND vaccines.
Figures


References
-
- Beal R. K., Wigley P., Powers C., Hulme S. D., Barrow P. A., Smith A. L.2004. Age at primary infection with Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in the chicken influences persistence of infection and subsequent immunity to re-challenge. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 100: 151–164. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2004.04.005 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Borden E. C., Hogan T. F., Voelkel J. G.1982. Comparative antiproliferative activity in vitro of natural interferons alpha and beta for diploid and transformed human cells. Cancer Res. 42: 4948–4953. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

