Down-regulation of Kelch domain-containing F-box protein in Arabidopsis enhances the production of (poly)phenols and tolerance to ultraviolet radiation
- PMID: 25502410
- PMCID: PMC4326750
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.114.249136
Down-regulation of Kelch domain-containing F-box protein in Arabidopsis enhances the production of (poly)phenols and tolerance to ultraviolet radiation
Abstract
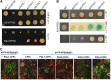
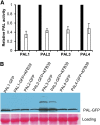
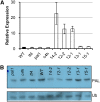
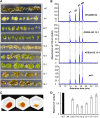
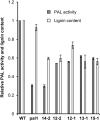
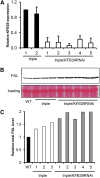
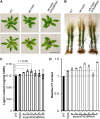
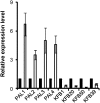
Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis in plants engenders myriad phenolics with diverse biological functions. Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) is the first committed enzyme in the pathway, directing primary metabolic flux into a phenylpropanoid branch. Previously, we demonstrated that the Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) Kelch domain-containing F-box proteins, AtKFB01, AtKFB20, and AtKFB50, function as the negative regulators controlling phenylpropanoid biosynthesis via mediating PAL's ubiquitination and subsequent degradation. Here, we reveal that Arabidopsis KFB39, a close homolog of AtKFB50, also interacts physically with PAL isozymes and modulates PAL stability and activity. Disturbing the expression of KFB39 reciprocally affects the accumulation/deposition of a set of phenylpropanoid end products, suggesting that KFB39 is an additional posttranslational regulator responsible for the turnover of PAL and negatively controlling phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. Furthermore, we discover that exposure of Arabidopsis to ultraviolet (UV)-B radiation suppresses the expression of all four KFB genes while inducing the transcription of PAL isogenes; these data suggest that Arabidopsis consolidates both transcriptional and posttranslational regulation mechanisms to maximize its responses to UV light stress. Simultaneous down-regulation of all four identified KFBs significantly enhances the production of (poly)phenols and the plant's tolerance to UV irradiation. This study offers a biotechnological approach for engineering the production of useful phenolic chemicals and for increasing a plant's resistance to environmental stress.
© 2015 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Post-translational and transcriptional regulation of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathway by Kelch repeat F-box protein SAGL1.Plant Mol Biol. 2019 Jan;99(1-2):135-148. doi: 10.1007/s11103-018-0808-8. Epub 2018 Dec 12. Plant Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30542810
-
Arabidopsis Kelch repeat F-box proteins regulate phenylpropanoid biosynthesis via controlling the turnover of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase.Plant Cell. 2013 Dec;25(12):4994-5010. doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.119644. Epub 2013 Dec 20. Plant Cell. 2013. PMID: 24363316 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of auxin and cytokinin responses by early steps of the phenylpropanoid pathway.BMC Plant Biol. 2018 Nov 12;18(1):278. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1477-0. BMC Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 30419822 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted regulations of gateway enzyme phenylalanine ammonia-lyase in the biosynthesis of phenylpropanoids.Mol Plant. 2015 Jan;8(1):17-27. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2014.11.001. Epub 2014 Dec 11. Mol Plant. 2015. PMID: 25578269 Review.
-
Mutants of Arabidopsis as tools to understand the regulation of phenylpropanoid pathway and UVB protection mechanisms.Photochem Photobiol. 1997 May;65(5):765-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1997.tb01923.x. Photochem Photobiol. 1997. PMID: 9155253 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Lignin Biosynthesis by Post-translational Protein Modifications.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Jul 2;11:914. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00914. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32714349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diverse and dynamic roles of F-box proteins in plant biology.Planta. 2020 Feb 18;251(3):68. doi: 10.1007/s00425-020-03356-8. Planta. 2020. PMID: 32072251 Review.
-
Aldoximes are precursors of auxins in Arabidopsis and maize.New Phytol. 2021 Aug;231(4):1449-1461. doi: 10.1111/nph.17447. Epub 2021 Jun 10. New Phytol. 2021. PMID: 33959967 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of small RNAs during cold acclimation in Arabidopsis thaliana.BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Jun 29;20(1):298. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02511-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 32600430 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide survey and expression analysis of F-box genes in chickpea.BMC Genomics. 2015 Feb 13;16(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1293-y. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25759239 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams J, Kelso R, Cooley L (2000) The Kelch repeat superfamily of proteins: propellers of cell function. Trends Cell Biol 10: 17–24 - PubMed
-
- Agati G, Azzarello E, Pollastri S, Tattini M (2012) Flavonoids as antioxidants in plants: location and functional significance. Plant Sci 196: 67–76 - PubMed
-
- Agati G, Tattini M (2010) Multiple functional roles of flavonoids in photoprotection. New Phytol 186: 786–793 - PubMed
-
- Bagchi D, Bagchi M, Stohs SJ, Das DK, Ray SD, Kuszynski CA, Joshi SS, Pruess HG (2000) Free radicals and grape seed proanthocyanidin extract: importance in human health and disease prevention. Toxicology 148: 187–197 - PubMed
-
- Bate NJ, Orr J, Ni W, Meromi A, Nadler-Hassar T, Doerner PW, Dixon RA, Lamb CJ, Elkind Y (1994) Quantitative relationship between phenylalanine ammonia-lyase levels and phenylpropanoid accumulation in transgenic tobacco identifies a rate-determining step in natural product synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 7608–7612 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

