Evidence revealing deregulation of the KLF11-MAO A pathway in association with chronic stress and depressive disorders
- PMID: 25502632
- PMCID: PMC4397395
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2014.321
Evidence revealing deregulation of the KLF11-MAO A pathway in association with chronic stress and depressive disorders
Abstract
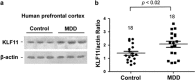
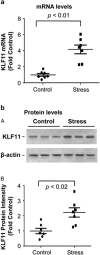
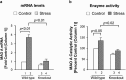
The biochemical pathways underlying major depressive disorder (MDD) and chronic stress are not well understood. However, it has been reported that monoamine oxidase A (MAO A, a major neurotransmitter-degrading enzyme) is significantly increased in the brains of human subjects affected with MDD and rats exposed to chronic social defeat (CSD) stress, which is used to model depression. In the current study, we compared the protein levels of a MAO A-transcriptional activator, Kruppel-like factor 11 (KLF11 , also recognized as transforming growth factor-beta-inducible early gene 2) between the brains of 18 human subjects with MDD and 18 control subjects. We found that, indeed, the expression of KLF11 is increased by 36% (p<0.02) in the postmortem prefrontal cortex of human subjects with MDD compared with controls. We also observed a positive correlation between KLF11 levels and those of its target gene, MAO A, both in association with MDD. KLF11 protein expression was also increased by 44% (p<0.02) in the frontal cortex of KLF11 wild-type mice (Klf11(+/+)) vs Klf11(-/-) when both exposed to CSD stress. In contrast, locomotor activities, central box duration and sucrose preference were significantly reduced in the stressed Klf11(+/+) mice, suggesting that Klf11(+/+) mice are more severely affected by the stress model compared with Klf11(-/-) mice. These results serve to assign an important role of KLF11 in upregulating MAO A in MDD and chronic social stress, suggesting that inhibition of the pathways regulated by this transcription factor may aid in the therapeutics of neuropsychiatric illnesses. Thus, the new knowledge derived from the current study extends our understanding of transcriptional mechanisms that are operational in the pathophysiology of common human diseases and thus bears significant biomedical relevance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanistic role for a novel glucocorticoid-KLF11 (TIEG2) protein pathway in stress-induced monoamine oxidase A expression.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jul 13;287(29):24195-206. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.373936. Epub 2012 May 24. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22628545 Free PMC article.
-
The expression of KLF11 (TIEG2), a monoamine oxidase B transcriptional activator in the prefrontal cortex of human alcohol dependence.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014 Jan;38(1):144-51. doi: 10.1111/acer.12229. Epub 2013 Aug 5. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014. PMID: 23915421 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes-causing gene, kruppel-like factor 11, modulates the antinociceptive response of chronic ethanol intake.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014 Feb;38(2):401-8. doi: 10.1111/acer.12258. Epub 2014 Jan 15. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014. PMID: 24428663 Free PMC article.
-
Monoamine oxidases in major depressive disorder and alcoholism.Drug Discov Ther. 2012 Jun;6(3):112-22. Drug Discov Ther. 2012. PMID: 22890201 Review.
-
The Distinct Roles of Transcriptional Factor KLF11 in Normal Cell Growth Regulation and Cancer as a Mediator of TGF-β Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 22;21(8):2928. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082928. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32331236 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulatory Pathways of Monoamine Oxidase A during Social Stress.Front Neurosci. 2017 Oct 31;11:604. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00604. eCollection 2017. Front Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29163009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contribution of serotonergic and nitrergic pathways, as well as monoamine oxidase-a and Na+, K+-ATPase enzymes in antidepressant-like action of ((4-tert-butylcyclohexylidene) methyl) (4-methoxystyryl) sulfide (BMMS).Metab Brain Dis. 2019 Oct;34(5):1313-1324. doi: 10.1007/s11011-019-00436-x. Epub 2019 Jun 8. Metab Brain Dis. 2019. PMID: 31177357
-
Mechanisms of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for anti-depression: Evidence from preclinical studies.World J Psychiatry. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):223-233. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v10.i10.223. eCollection 2020 Oct 19. World J Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 33134113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic Social Stress and Ethanol Increase Expression of KLF11, a Cell Death Mediator, in Rat Brain.Neurotox Res. 2015 Jul;28(1):18-31. doi: 10.1007/s12640-015-9524-1. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Neurotox Res. 2015. PMID: 25739536 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Roles of microRNAs in the Regulation of Monoamine Oxidase A in the Brain.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 Sep 14;11:339. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00339. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30271325 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andreazza AC, Shao L, Wang JF, Young LT. Mitochondrial complex I activity and oxidative damage to mitochondrial proteins in the prefrontal cortex of patients with bipolar disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010;67:360–368. - PubMed
-
- Bacher I, Houle S, Xu X, Zawertailo L, Soliman A, Wilson AA, et al. Monoamine oxidase A binding in the prefrontal and anterior cingulate cortices during acute withdrawal from heavy cigarette smoking. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2011;68:817–826. - PubMed
-
- Barr AM, Young CE, Sawada K, Trimble WS, Phillips AG, Honer WG. Abnormalities of presynaptic protein CDCrel-1 in striatum of rats reared in social isolation: relevance to neural connectivity in schizophrenia. Eur J Neurosci. 2004;20:303–307. - PubMed
-
- Beasley CL, Honer WG, Bergmann K, Falkai P, Lutjohann D, Bayer TA. Reductions in cholesterol and synaptic markers in association cortex in mood disorders. Bipolar Disord. 2005;7:449–455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

