Crystal structure of calcium binding protein-5 from Entamoeba histolytica and its involvement in initiation of phagocytosis of human erythrocytes
- PMID: 25502654
- PMCID: PMC4263763
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004532
Crystal structure of calcium binding protein-5 from Entamoeba histolytica and its involvement in initiation of phagocytosis of human erythrocytes
Erratum in
-
Correction: Crystal structure of calcium binding protein-5 from Entamoeba histolytica and its involvement in initiation of phagocytosis of human erythrocytes.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Mar 27;11(3):e1004716. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004716. eCollection 2015 Mar. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 25816121 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
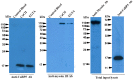
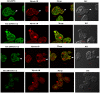
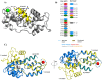
Entamoeba histolytica is the etiological agent of human amoebic colitis and liver abscess, and causes a high level of morbidity and mortality worldwide, particularly in developing countries. There are a number of studies that have shown a crucial role for Ca2+ and its binding protein in amoebic biology. EhCaBP5 is one of the EF hand calcium-binding proteins of E. histolytica. We have determined the crystal structure of EhCaBP5 at 1.9 Å resolution in the Ca2+-bound state, which shows an unconventional mode of Ca2+ binding involving coordination to a closed yet canonical EF-hand motif. Structurally, EhCaBP5 is more similar to the essential light chain of myosin than to Calmodulin despite its somewhat greater sequence identity with Calmodulin. This structure-based analysis suggests that EhCaBP5 could be a light chain of myosin. Surface plasmon resonance studies confirmed this hypothesis, and in particular showed that EhCaBP5 interacts with the IQ motif of myosin 1B in calcium independent manner. It also appears from modelling of the EhCaBP5-IQ motif complex that EhCaBP5 undergoes a structural change in order to bind the IQ motif of myosin. This specific interaction was further confirmed by the observation that EhCaBP5 and myosin 1B are colocalized in E. histolytica during phagocytic cup formation. Immunoprecipitation of EhCaBP5 from total E. histolytica cellular extract also pulls out myosin 1B and this interaction was confirmed to be Ca2+ independent. Confocal imaging of E. histolytica showed that EhCaBP5 and myosin 1B are part of phagosomes. Overexpression of EhCaBP5 increases slight rate (∼20%) of phagosome formation, while suppression reduces the rate drastically (∼55%). Taken together, these experiments indicate that EhCaBP5 is likely to be the light chain of myosin 1B. Interestingly, EhCaBP5 is not present in the phagosome after its formation suggesting EhCaBP5 may be playing a regulatory role.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Entamoeba histolytica and pathogenesis: A calcium connection.PLoS Pathog. 2020 May 7;16(5):e1008214. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008214. eCollection 2020 May. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32379809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Calmodulin-like calcium binding protein EhCaBP3 of Entamoeba histolytica regulates phagocytosis and is involved in actin dynamics.PLoS Pathog. 2012 Dec;8(12):e1003055. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003055. Epub 2012 Dec 27. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 23300437 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-binding protein EhCaBP3 is recruited to the phagocytic complex of Entamoeba histolytica by interacting with Arp2/3 complex subunit 2.Cell Microbiol. 2018 Dec;20(12):e12942. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12942. Epub 2018 Sep 7. Cell Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30133964
-
The Monomeric GTPase Rab35 Regulates Phagocytic Cup Formation and Phagosomal Maturation in Entamoeba histolytica.J Biol Chem. 2017 Mar 24;292(12):4960-4975. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.775007. Epub 2017 Jan 26. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28126902 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the role of the cytoskeleton in phagocytosis of Entamoeba histolytica.Cell Microbiol. 1999 Nov;1(3):195-203. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-5822.1999.00021.x. Cell Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 11207552 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular interplays of the Entamoeba histolytica endosomal sorting complexes required for transport during phagocytosis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Oct 27;12:855797. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.855797. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36389174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure of Ca2+-binding protein-6 from Entamoeba histolytica and its involvement in trophozoite proliferation regulation.PLoS Pathog. 2017 May 15;13(5):e1006332. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006332. eCollection 2017 May. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28505197 Free PMC article.
-
Chew on this: amoebic trogocytosis and host cell killing by Entamoeba histolytica.Trends Parasitol. 2015 Sep;31(9):442-52. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2015.05.003. Epub 2015 Jun 9. Trends Parasitol. 2015. PMID: 26070402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Entamoeba histolytica and pathogenesis: A calcium connection.PLoS Pathog. 2020 May 7;16(5):e1008214. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008214. eCollection 2020 May. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32379809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure-Function Diversity of Calcium-Binding Proteins (CaBPs): Key Roles in Cell Signalling and Disease.Cells. 2025 Jan 21;14(3):152. doi: 10.3390/cells14030152. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39936944 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO/PAHO/UNESCO report. A consultation with experts on amoebiasis. Mexico City, Mexico 28–29 January, 1997. Epidemiol Bull 18: 13–14. - PubMed
-
- Stanley SL Jr (2003) Amoebiasis. Lancet 361: 1025–1034. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharya A, Padhan N, Jain R, Bhattacharya S (2006) Calcium-binding proteins of Entamoeba histolytica. Arch Med Res 37: 221–225. - PubMed
-
- Sahoo N, Labruyere E, Bhattacharya S, Sen P, Guillen N, et al. (2004) Calcium binding protein 1 of the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica interacts with actin and is involved in cytoskeleton dynamics. J Cell Sci 117: 3625–3634. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

