Egr-1 activation by cancer-derived extracellular vesicles promotes endothelial cell migration via ERK1/2 and JNK signaling pathways
- PMID: 25502753
- PMCID: PMC4264882
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115170
Egr-1 activation by cancer-derived extracellular vesicles promotes endothelial cell migration via ERK1/2 and JNK signaling pathways
Abstract
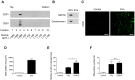
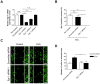
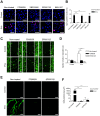
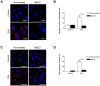
Various mammalian cells, including cancer cells, shed extracellular vesicles (EVs), also known as exosomes and microvesicles, into surrounding tissues. These EVs play roles in tumor growth and metastasis by promoting angiogenesis. However, the detailed mechanism of how cancer-derived EVs elicit endothelial cell activation remains unknown. Here, we provide evidence that early growth response-1 (Egr-1) activation in endothelial cells is involved in the angiogenic activity of colorectal cancer cell-derived EVs. Both RNA interference-mediated downregulation of Egr-1 and ERK1/2 or JNK inhibitor significantly blocked EV-mediated Egr-1 activation and endothelial cell migration. Furthermore, lipid raft-mediated endocytosis inhibitor effectively blocked endothelial Egr-1 activation and migration induced by cancer-derived EVs. Our results suggest that Egr-1 activation in endothelial cells may be a key mechanism involved in the angiogenic activity of cancer-derived EVs. These findings will improve our understanding regarding the proangiogenic activities of EVs in diverse pathological conditions including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and neurodegenerative diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Extracellular Vesicles Activate a CD36-Dependent Signaling Pathway to Inhibit Microvascular Endothelial Cell Migration and Tube Formation.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 Mar;36(3):534-44. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.307085. Epub 2016 Jan 28. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 26821945 Free PMC article.
-
Early growth response-1 regulates angiopoietin-1-induced endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009 Feb;29(2):209-16. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.108.181073. Epub 2008 Dec 26. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009. PMID: 19112164
-
Pro-Angiogenic Actions of CMC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Rely on Selective Packaging of Angiopoietin 1 and 2, but Not FGF-2 and VEGF.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2019 Aug;15(4):530-542. doi: 10.1007/s12015-019-09891-6. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2019. PMID: 31102187 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicle docking at the cellular port: Extracellular vesicle binding and uptake.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Jul;67:48-55. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.01.002. Epub 2017 Jan 16. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28104520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicle communication pathways as regulatory targets of oncogenic transformation.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Jul;67:11-22. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.01.003. Epub 2017 Jan 8. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28077296 Review.
Cited by
-
Rapamycin-induced autophagy protects proximal tubular renal cells against proteinuric damage through the transcriptional activation of the nerve growth factor receptor NGFR.Autophagy. 2018;14(6):1028-1042. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2018.1448740. Epub 2018 May 11. Autophagy. 2018. PMID: 29749806 Free PMC article.
-
A Snapshot of The Tumor Microenvironment in Colorectal Cancer: The Liquid Biopsy.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 29;20(23):6016. doi: 10.3390/ijms20236016. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31795332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic Profiling of Tissue Exosomes Indicates Continuous Release of Malignant Exosomes in Urinary Bladder Cancer Patients, Even with Pathologically Undetectable Tumour.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jun 29;13(13):3242. doi: 10.3390/cancers13133242. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34209558 Free PMC article.
-
VE-cadherin cleavage by ovarian cancer microparticles induces β-catenin phosphorylation in endothelial cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Feb 2;7(5):5289-305. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6677. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26700621 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Transcription Factor EGR1 in Cancer.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 24;11:642547. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.642547. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33842351 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ratajczak J, Wysoczynski M, Hayek F, Janowska-Wieczorek A, Ratajczak MZ (2006) Membrane-derived microvesicles: important and underappreciated mediators of cell-to-cell communication. Leukemia 20 (9):1487–1495. - PubMed
-
- Cocucci E, Racchetti G, Meldolesi J (2009) Shedding microvesicles: artefacts no more. Trends Cell Biol 19 (2):43–51. - PubMed
-
- Bobrie A, Colombo M, Raposo G, Thery C (2011) Exosome secretion: molecular mechanisms and roles in immune responses. Traffic 12 (12):1659–1668. - PubMed
-
- Choi DS, Kim DK, Kim YK, Gho YS (2013) Proteomics, transcriptomics and lipidomics of exosomes and ectosomes. Proteomics. - PubMed
-
- Kim CW, Lee HM, Lee TH, Kang C, Kleinman HK, et al. (2002) Extracellular membrane vesicles from tumor cells promote angiogenesis via sphingomyelin. Cancer Res 62 (21):6312–6317. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

