Instability of misoprostol tablets stored outside the blister: a potential serious concern for clinical outcome in medical abortion
- PMID: 25502819
- PMCID: PMC4266501
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112401
Instability of misoprostol tablets stored outside the blister: a potential serious concern for clinical outcome in medical abortion
Abstract
Introduction: Misoprostol (Cytotec) is recognised to be effective for many gynaecological indications including termination of pregnancy, management of miscarriage and postpartum haemorrhage. Although not licensed for such indications, it has been used for these purposes by millions of women throughout the world. Misoprostol tablets are most often packaged as multiple tablets within an aluminium strip, each within an individual alveolus. When an alveolus is opened, tablets will be exposed to atmospheric conditions.
Objective: To compare the pharmaco technical characteristics (weight, friability), water content, misoprostol content and decomposition product content (type A misoprostol, type B misoprostol and 8-epi misoprostol) of misoprostol tablets Cytotec (Pfizer) exposed to air for periods of 1 hour to 720 hours (30 days), to those of identical non exposed tablets.
Methods: Four hundred and twenty (420) tablets of Cytotec (Pfizer) were removed from their alveoli blister and stored at 25°C/60% relative humidity. Water content, and misoprostol degradation products were assayed in tablets exposed from 1 to 720 hours (30 days). Comparison was made with control tablets (N=60) from the same batch stored in non-damaged blisters. Statistical analyses were carried out using Fisher's exact test for small sample sizes.
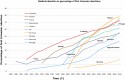
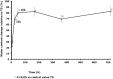
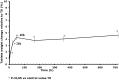
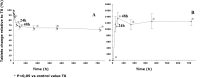
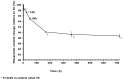
Results: By 48 hours, exposed tablets demonstrated increased weight (+4.5%), friability (+1 300%), and water content (+80%) compared to controls. Exposed tablets also exhibited a decrease in Cytotec active ingredient dosage (-5.1% after 48 hours) and an increase in the inactive degradation products (+25% for type B, +50% for type A and +11% for 8-epi misoprostol after 48 hours) compared to controls.
Conclusion: Exposure of Cytotec tablets to 'typical' European levels of air and humidity results in significant time-dependent changes in physical and biological composition that could impact adversely upon clinical efficacy. Health professionals should be made aware of the degradation of misoprostol with inappropriate storage of misoprostol tablets.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Creinin M (2000) Medical abortion regimens: historical context and overview. Am J Obstet Gynecol 183:S3–S9. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard K, Clark S, Winikoff B, Gaines G, Kabani G, et al. (2002) Misoprostol for women’s health: A review. Am J Obstet Gynecol 99(2):316–332. - PubMed
-
- Shaw D, Tang OS, Gemzell-Danielsson K, Ho PC, Fiala C, et al. (2007) Misoprostol for Reproductive Health. Int J of Gynecology & Obstetrics 99:S155–205.
-
- Herabutya Y, O-Prasertsawat P (1997) Misoprostol in the management of missed abortion. Int J Gynecol Obstet 56:263–6. - PubMed
-
- Chung T, Leung P, Cheung LP, Haines C, Chang AM (1997) A medical approach to management of spontaneous abortion using misoprostol. Extending misoprostol treatment to a maximum of 48 hours can further improve evacuation of retained products of conception in spontaneous abortion. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 76:248–51. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

