Unconscious local motion alters global image speed
- PMID: 25503603
- PMCID: PMC4266498
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112804
Unconscious local motion alters global image speed
Abstract
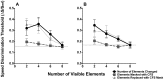
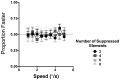
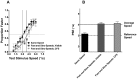
Accurate motion perception of self and object speed is crucial for successful interaction in the world. The context in which we make such speed judgments has a profound effect on their accuracy. Misperceptions of motion speed caused by the context can have drastic consequences in real world situations, but they also reveal much about the underlying mechanisms of motion perception. Here we show that motion signals suppressed from awareness can warp simultaneous conscious speed perception. In Experiment 1, we measured global speed discrimination thresholds using an annulus of 8 local Gabor elements. We show that physically removing local elements from the array attenuated global speed discrimination. However, removing awareness of the local elements only had a small effect on speed discrimination. That is, unconscious local motion elements contributed to global conscious speed perception. In Experiment 2 we measured the global speed of the moving Gabor patterns, when half the elements moved at different speeds. We show that global speed averaging occurred regardless of whether local elements were removed from awareness, such that the speed of invisible elements continued to be averaged together with the visible elements to determine the global speed. These data suggest that contextual motion signals outside of awareness can both boost and affect our experience of motion speed, and suggest that such pooling of motion signals occurs before the conscious extraction of the surround motion speed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Global speed processing: evidence for local averaging within, but not across two speed ranges.Vision Res. 2002 Dec;42(28):3031-42. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6989(02)00384-x. Vision Res. 2002. PMID: 12480073
-
Spatial-frequency tuning in the pooling of one- and two-dimensional motion signals.Vision Res. 2009 Nov;49(23):2862-9. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2009.08.026. Epub 2009 Sep 2. Vision Res. 2009. PMID: 19732787
-
Contrast effects on speed perception for linear and radial motion.Vision Res. 2017 Nov;140:66-72. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2017.07.013. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Vision Res. 2017. PMID: 28822716
-
Motion grouping impairs speed discrimination.Vision Res. 2006 Apr;46(8-9):1540-6. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2005.07.029. Epub 2005 Sep 13. Vision Res. 2006. PMID: 16168457
-
Local form-motion interactions influence global form perception.Atten Percept Psychophys. 2012 Jul;74(5):816-23. doi: 10.3758/s13414-012-0307-y. Atten Percept Psychophys. 2012. PMID: 22528613
References
-
- Nishida S (2011) Advancement of motion psychophysics: review 2001–2010. J Vis 11(5):p 11. - PubMed
-
- Adelson EH, Movshon JA (1982) Phenomenal coherence of moving visual patterns. Nature 300(5892):p 523–5. - PubMed
-
- Orban GA, Lagae L, Raiquel S, Xiao D, Maes H (1995) The speed tuning of medial superior temporal (MST) cell responses to optic-flow components. Perception 24(3):p 269–85. - PubMed
-
- Kim CY, Blake R (2005) Psychophysical magic: rendering the visible ‘invisible’. Trends Cogn Sci 9(8):p 381–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

