Vitamin D receptor agonist VS-105 improves cardiac function in the presence of enalapril in 5/6 nephrectomized rats
- PMID: 25503724
- PMCID: PMC4329489
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00129.2014
Vitamin D receptor agonist VS-105 improves cardiac function in the presence of enalapril in 5/6 nephrectomized rats
Abstract
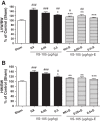
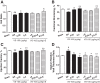
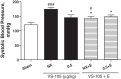
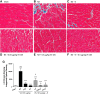
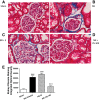
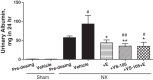
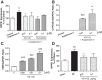
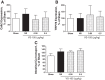
Vitamin D receptor (VDR) agonists (VDRAs) are commonly used to manage hyperparathyroidism secondary to chronic kidney disease (CKD). Patients with CKD experience extremely high risks of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Clinical observations show that VDRA therapy may be associated with cardio-renal protective and survival benefits in patients with CKD. The 5/6 nephrectomized (NX) Sprague-Dawley rat with established uremia exhibits elevated serum parathyroid hormone (PTH), hypertension, and abnormal cardiac function. Treatment of 5/6 NX rats with VS-105, a novel VDRA (0.05 and 0.5 μg/kg po by gavage), once daily for 8 wk in the presence or absence of enalapril (30 mg/kg po via drinking water) effectively suppressed serum PTH without raising serum calcium. VS-105 alone reduced systolic blood pressure (from 174 ± 6 to 145 ± 9 mmHg, P < 0.05) as effectively as enalapril (from 174 ± 6 to 144 ± 7 mmHg, P < 0.05). VS-105 improved cardiac functional parameters such as E/A ratio, ejection fraction, and fractional shortening with or without enalapril. Enalapril or VS-105 alone significantly reduced left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH); VS-105 plus enalapril did not further reduce LVH. VS-105 significantly reduced both cardiac and renal fibrosis. The lack of hypercalcemic toxicity of VS-105 is due to its lack of effects on stimulating intestinal calcium transport and inducing the expression of intestinal calcium transporter genes such as Calb3 and TRPV6. These studies demonstrate that VS-105 is a novel VDRA that may provide cardiovascular benefits via VDR activation. Clinical studies are required to confirm the cardiovascular benefits of VS-105 in CKD.
Keywords: PTH; cardiac function; chronic kidney disease; vitamin D analog; vitamin D receptor.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
VS-105: a novel vitamin D receptor modulator with cardiovascular protective effects.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Sep;164(2b):551-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01473.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21557735 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D receptor agonist VS-105 directly modulates parathyroid hormone expression in human parathyroid cells and in 5/6 nephrectomized rats.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017 Mar;167:48-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.10.008. Epub 2016 Oct 29. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27989797
-
Two novel vitamin D receptor modulators with similar structures exhibit different hypercalcemic effects in 5/6 nephrectomized uremic rats.Am J Nephrol. 2013;37(4):310-9. doi: 10.1159/000348755. Epub 2013 Mar 20. Am J Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23548814
-
Hypertension and Organ Damage in Women.High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2018 Sep;25(3):245-252. doi: 10.1007/s40292-018-0265-0. Epub 2018 Jun 26. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2018. PMID: 29943358 Review.
-
Different vitamin D receptor agonists exhibit differential effects on endothelial function and aortic gene expression in 5/6 nephrectomized rats.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015 Apr;148:202-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.12.002. Epub 2014 Dec 10. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25500070 Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel Vitamin D Receptor Agonist, VS-105, Improves Bone Mineral Density without Affecting Serum Calcium in a Postmenopausal Osteoporosis Rat Model.J Explor Res Pharmacol. 2020 Dec;5(4):73-80. doi: 10.14218/jerp.2020.00020. Epub 2020 Nov 6. J Explor Res Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 34589670 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D Effects on Bone Homeostasis and Cardiovascular System in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Renal Transplant Recipients.Nutrients. 2021 Apr 25;13(5):1453. doi: 10.3390/nu13051453. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33922902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Qingshen Buyang Formula Attenuates Renal Fibrosis in 5/6 Nephrectomized Rats via Inhibiting EMT and Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 May 2;2019:5370847. doi: 10.1155/2019/5370847. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31186661 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D treatment attenuates cardiac FGF23/FGFR4 signaling and hypertrophy in uremic rats.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2017 Sep 1;32(9):1493-1503. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfw454. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2017. PMID: 28339837 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnaout MS, Alam SE. Congestive heart failure: new paradigms and therapeutic targets. J Med Liban 51: 169–175, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Baigent C, Burbury K, Wheeler D. Premature cardiovascular disease in chronic renal failure. Lancet 356: 147–152, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Bertrand ME. Provision of cardiovascular protection by ACE inhibitors: a review of recent trials. Curr Med Res Opin 20: 1559–1569, 2004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

