Differential expression of cytochrome P450 enzymes from the CYP2C subfamily in the human brain
- PMID: 25504503
- PMCID: PMC6067382
- DOI: 10.1124/dmd.114.061242
Differential expression of cytochrome P450 enzymes from the CYP2C subfamily in the human brain
Abstract
Cytochrome P450 enzymes from the CYP2C subfamily play a prominent role in the metabolic clearance of many drugs. CYP2C enzymes have also been implicated in the metabolism of arachidonic acid to vasoactive epoxyeicosatrienoic acids. CYP2C8, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19 are expressed in the adult liver at significant levels; however, the expression of CYP2C enzymes in extrahepatic tissues such as the brain is less well characterized. Form-specific antibodies to CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 were prepared by affinity purification of antibodies raised to unique peptides. CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 were located in microsomal fractions of all five human brain regions examined, namely the frontal cortex, hippocampus, basal ganglia, amygdala, and cerebellum. Both CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 were detected predominantly within the neuronal soma but with expression extending down axons and dendrites in certain regions. Finally, a comparison of cortex samples from alcoholics and age-matched controls suggested that CYP2C9 expression was increased in alcoholics.
Copyright © 2015 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures

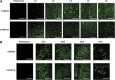
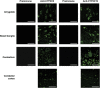
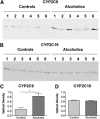
Similar articles
-
Arachidonic acid metabolism by human cytochrome P450s 2C8, 2C9, 2E1, and 1A2: regioselective oxygenation and evidence for a role for CYP2C enzymes in arachidonic acid epoxygenation in human liver microsomes.Arch Biochem Biophys. 1995 Jul 10;320(2):380-9. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(95)90023-3. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1995. PMID: 7625847
-
Differential expression and function of CYP2C isoforms in human intestine and liver.Pharmacogenetics. 2003 Sep;13(9):565-75. doi: 10.1097/00008571-200309000-00005. Pharmacogenetics. 2003. PMID: 12972955
-
CYP2C19 participates in tolbutamide hydroxylation by human liver microsomes.Drug Metab Dispos. 2000 Mar;28(3):354-9. Drug Metab Dispos. 2000. PMID: 10681382
-
Comparison of cytochrome P450 2C subfamily members in terms of drug oxidation rates and substrate inhibition.Curr Drug Metab. 2012 Oct;13(8):1145-59. doi: 10.2174/138920012802850092. Curr Drug Metab. 2012. PMID: 22571484 Review.
-
The transcriptional regulation of the human CYP2C genes.Curr Drug Metab. 2009 Jul;10(6):567-78. doi: 10.2174/138920009789375397. Epub 2009 Jul 15. Curr Drug Metab. 2009. PMID: 19702536 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of efflux transporters and metabolizing enzymes in brain and peripheral organs to explain drug-resistant epilepsy.Epilepsia Open. 2022 Aug;7 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S47-S58. doi: 10.1002/epi4.12542. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Epilepsia Open. 2022. PMID: 34560816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic tracking of disrupted modules identifies significant genes and pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2016 Nov;12(5):3285-3295. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.5039. Epub 2016 Aug 23. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27899995 Free PMC article.
-
CYP2C19 variant mitigates Alzheimer disease pathophysiology in vivo and postmortem.Neurol Genet. 2018 Jan 30;4(1):e216. doi: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000216. eCollection 2018 Feb. Neurol Genet. 2018. PMID: 29473050 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphic variants of drug-metabolizing enzymes alter the risk and survival of oral cancer patients.3 Biotech. 2020 Dec;10(12):529. doi: 10.1007/s13205-020-02526-5. Epub 2020 Nov 12. 3 Biotech. 2020. PMID: 33214976 Free PMC article.
-
Dihydroxy-Metabolites of Dihomo-gamma-linolenic Acid Drive Ferroptosis-Mediated Neurodegeneration.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jan 10:2023.01.05.522933. doi: 10.1101/2023.01.05.522933. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: ACS Cent Sci. 2023 Mar 16;9(5):870-882. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.3c00052. PMID: 36711920 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Alkayed NJ, Birks EK, Hudetz AG, Roman RJ, Henderson L, Harder DR. (1996) Inhibition of brain P-450 arachidonic acid epoxygenase decreases baseline cerebral blood flow. Am J Physiol 271:H1541–H1546. - PubMed
-
- Booth Depaz IM, Toselli F, Wilce PA, Gillam EM. (2013) Differential expression of human cytochrome P450 enzymes from the CYP3A subfamily in the brains of alcoholic subjects and drug-free controls. Drug Metab Dispos 41:1187–1194. - PubMed
-
- Cuttle L, Munns AJ, Hogg NA, Scott JR, Hooper WD, Dickinson RG, Gillam EMJ. (2000) Phenytoin metabolism by human cytochrome P450: involvement of P450 3A and 2C forms in secondary metabolism and drug-protein adduct formation. Drug Metab Dispos 28:945–950. - PubMed
-
- Dauchy S, Dutheil F, Weaver RJ, Chassoux F, Daumas-Duport C, Couraud PO, Scherrmann JM, De Waziers I, Declèves X. (2008) ABC transporters, cytochromes P450 and their main transcription factors: expression at the human blood-brain barrier. J Neurochem 107:1518–1528. - PubMed
-
- Dauchy S, Miller F, Couraud P-O, Weaver RJ, Weksler B, Romero I-A, Scherrmann J-M, De Waziers I, Decleves X. (2009) Expression and transcriptional regulation of ABC transporters and cytochromes P450 in hCMEC/D3 human cerebral microvascular endothelial cells. Biochem Pharmacol 77:897–909. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

