Cell-based Models To Investigate Tau Aggregation
- PMID: 25505502
- PMCID: PMC4262059
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2014.09.011
Cell-based Models To Investigate Tau Aggregation
Abstract
Accumulation of abnormal tau aggregates in neuron is an important pathological signature in multiple neurodegenerative disorders including Alzheimer's disease. Tau is a neuron specific microtubule-associated protein that regulates microtubule stability, which is critical for axonal outgrowth and synaptic plasticity. In a pathological condition, tau dissociates from microtubules and forms insoluble aggregates called neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs). The accumulation of NFTs in neuron directly correlates with microtubule dysfunction and neuronal degeneration. Due to the pathophysiological importance of tau, great efforts have been made to understand tau aggregation processes and find therapeutics to halt or reverse the processes. However, progress has been slow due to the lack of a suitable method for monitoring tau aggregation. In this mini-review, we will review the conventional methods for studying tau aggregation, and introduce recent cell-based sensor approaches that allow monitoring tau aggregation in living cells.
Keywords: BiFC; Cell-based sensor; In vitro assay; Tau oligomerization; Tau phosphorylation; Tauopathy.
Figures


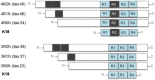


References
-
- Binder L.I., Guillozet-Bongaarts A.L., Garcia-Sierra F., Berry R.W. Tau, tangles, and Alzheimer's disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1739:216–223. - PubMed
-
- Johnson G.V., Hartigan J.A. Tau protein in normal and Alzheimer's disease brain: an update. J Alzheimers Dis. 1999;1:329–351. - PubMed
-
- Brandt R., Hundelt M., Shahani N. Tau alteration and neuronal degeneration in tauopathies: mechanisms and models. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1739:331–354. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
