NL-103, a novel dual-targeted inhibitor of histone deacetylases and hedgehog pathway, effectively overcomes vismodegib resistance conferred by Smo mutations
- PMID: 25505589
- PMCID: PMC4186412
- DOI: 10.1002/prp2.43
NL-103, a novel dual-targeted inhibitor of histone deacetylases and hedgehog pathway, effectively overcomes vismodegib resistance conferred by Smo mutations
Abstract
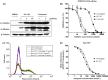
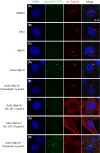
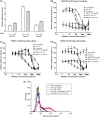
Misregulation of hedgehog (Hh) signaling has been implicated in the pathogenesis of basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and medulloblastoma. Vismodegib, an orally bioavailable Hh signal pathway inhibitor targeting Smo, has been approved for the treatment of advanced BCC. However, acquired drug resistance to vismodegib induced by point mutation in Smo is emerging as a major problem to vismodegib treatment. In this study, we designed and synthesized a novel chimeric compound NL-103, which comprises structural elements of Hh pathway inhibitor vismodegib, and histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor vorinostat. NL-103 simultaneously and significantly inhibited both HDACs and Hh pathway. Importantly, NL-103, as well as vorinostat, effectively overcame vismodegib resistance induced by Smoothened point mutations. Moreover, NL-103 and vorinostat, but not vismodegib, significantly downregulated the expression of Gli2 which plays an important role in Hh pathway. These results indicate that HDAC inhibitory activity is essential for NL-103 to overcome vismodegib resistance and that dual inhibition of HDAC and Hh signaling pathway may be a rational strategy for overcoming vismodegib resistance. Our findings suggest that NL-103 may be a promising compound for clinical development as a more effective Hh pathway inhibitor.
Keywords: Drug resistance; NL-103; hedgehog pathway inhibitor; histone deacetylase inhibitor; smoothened mutation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Vismodegib: an inhibitor of the Hedgehog signaling pathway in the treatment of basal cell carcinoma.Ann Pharmacother. 2014 Jan;48(1):99-106. doi: 10.1177/1060028013506696. Epub 2013 Oct 15. Ann Pharmacother. 2014. PMID: 24259609 Review.
-
Targeting class I histone deacetylases by the novel small molecule inhibitor 4SC-202 blocks oncogenic hedgehog-GLI signaling and overcomes smoothened inhibitor resistance.Int J Cancer. 2018 Mar 1;142(5):968-975. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31117. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Int J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29055107 Free PMC article.
-
A sterol analog inhibits hedgehog pathway by blocking cholesterylation of smoothened.Cell Chem Biol. 2024 Jul 18;31(7):1264-1276.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2024.02.002. Epub 2024 Mar 4. Cell Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 38442710
-
Discovery and preclinical development of vismodegib.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2014 Aug;9(8):969-84. doi: 10.1517/17460441.2014.920816. Epub 2014 May 23. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2014. PMID: 24857041 Review.
-
L-4, a Well-Tolerated and Orally Active Inhibitor of Hedgehog Pathway, Exhibited Potent Anti-tumor Effects Against Medulloblastoma in vitro and in vivo.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Feb 21;10:89. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00089. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30846937 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Non-canonical Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Cancer: Activation of GLI Transcription Factors Beyond Smoothened.Front Genet. 2019 Jun 12;10:556. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00556. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31244888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic polypharmacology: from combination therapy to multitargeted drugs.Clin Epigenetics. 2016 Oct 12;8:105. doi: 10.1186/s13148-016-0271-9. eCollection 2016. Clin Epigenetics. 2016. PMID: 27752293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hedgehog Signaling in Myeloid Malignancies.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Sep 29;13(19):4888. doi: 10.3390/cancers13194888. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34638372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A synthetic combinatorial approach to disabling deviant Hedgehog signaling.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 18;8(1):1133. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19408-9. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29348431 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic Small Molecule Inhibitors of Hh Signaling As Anti-Cancer Chemotherapeutics.Curr Med Chem. 2015;22(35):4033-57. doi: 10.2174/0929867322666150827093904. Curr Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26310919 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bai CB, Joyner AL. Gli1 can rescue the in vivo function of Gli2. Development. 2001;128:5161–5172. - PubMed
-
- Bai CB, Auerbach W, Lee JS, Stephen D, Joyner AL. Gli2, but not Gli1, is required for initial Shh signaling and ectopic activation of the Shh pathway. Development. 2002;129:4753–4761. - PubMed
-
- Bolden JE, Peart MJ, Johnstone RW. Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. 2006;5:769–784. - PubMed
-
- Cai X, Zhai H-X, Wang J, Forrester J, Qu H, Yin L, et al. Discovery of 7-(4-(3-ethynylphenylamino)-7-methoxyquinazolin-6-yloxy)-N-hydroxyheptanamide (CUDC-101) as a potent multi-acting HDAC, EGFR, and HER2 inhibitor for the treatment of cancer. J Med Chem. 2010;53:2000–2009. - PubMed
-
- Canettieri G, Di Marcotullio L, Greco A, Coni S, Antonucci L, Infante P, et al. Histone deacetylase and Cullin3–RENKCTD11 ubiquitin ligase interplay regulates Hedgehog signalling through Gli acetylation. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12:132–142. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

