Quantitative Comparison of SPM, FSL, and Brainsuite for Brain MR Image Segmentation
- PMID: 25505764
- PMCID: PMC4258855
Quantitative Comparison of SPM, FSL, and Brainsuite for Brain MR Image Segmentation
Abstract
Background: Accurate brain tissue segmentation from magnetic resonance (MR) images is an important step in analysis of cerebral images. There are software packages which are used for brain segmentation. These packages usually contain a set of skull stripping, intensity non-uniformity (bias) correction and segmentation routines. Thus, assessment of the quality of the segmented gray matter (GM), white matter (WM) and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is needed for the neuroimaging applications.
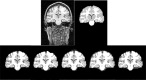
Methods: In this paper, performance evaluation of three widely used brain segmentation software packages SPM8, FSL and Brainsuite is presented. Segmentation with SPM8 has been performed in three frameworks: i) default segmentation, ii) SPM8 New-segmentation and iii) modified version using hidden Markov random field as implemented in SPM8-VBM toolbox.
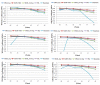
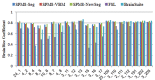
Results: The accuracy of the segmented GM, WM and CSF and the robustness of the tools against changes of image quality has been assessed using Brainweb simulated MR images and IBSR real MR images. The calculated similarity between the segmented tissues using different tools and corresponding ground truth shows variations in segmentation results.
Conclusion: A few studies has investigated GM, WM and CSF segmentation. In these studies, the skull stripping and bias correction are performed separately and they just evaluated the segmentation. Thus, in this study, assessment of complete segmentation framework consisting of pre-processing and segmentation of these packages is performed. The obtained results can assist the users in choosing an appropriate segmentation software package for the neuroimaging application of interest.
Keywords: Brain; Brainsuite; FSL; MRI; SPM; Segmentation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
3D cerebral MR image segmentation using multiple-classifier system.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2017 Mar;55(3):353-364. doi: 10.1007/s11517-016-1483-z. Epub 2016 May 20. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2017. PMID: 27207464
-
Comparison of Multispectral Image-Processing Methods for Brain Tissue Classification in BrainWeb Synthetic Data and Real MR Images.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Mar 7;2021:9820145. doi: 10.1155/2021/9820145. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33748284 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of whole brain segmentation and volume estimation in children and young adults using SPM and SyMRI.Clin Imaging. 2019 Sep-Oct;57:77-82. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2019.05.008. Epub 2019 May 21. Clin Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31136882
-
Methods on Skull Stripping of MRI Head Scan Images-a Review.J Digit Imaging. 2016 Jun;29(3):365-79. doi: 10.1007/s10278-015-9847-8. J Digit Imaging. 2016. PMID: 26628083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Testable Hypotheses for Unbalanced Neuroimaging Data.Front Neurosci. 2016 Jun 17;10:270. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2016.00270. eCollection 2016. Front Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27378839 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Caution: shortcomings of traditional segmentation methods from magnetic resonance imaging brain scans intended for 3-dimensional surface modelling in children with pathology.Pediatr Radiol. 2023 Aug;53(9):1854-1862. doi: 10.1007/s00247-023-05692-9. Epub 2023 May 30. Pediatr Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37249622 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Gait Analysis Indicate Similar Outcomes Between Yucatan and Landrace Porcine Ischemic Stroke Models.Front Neurol. 2021 Jan 21;11:594954. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.594954. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33551956 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging techniques for indirect assessment of myelin content in the brain using standard T1w and T2w MRI sequences and postprocessing analysis.Physiol Res. 2023 Dec 29;72(S5):S573-S585. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.935250. Physiol Res. 2023. PMID: 38165761 Free PMC article.
-
Repeatability and reproducibility of FreeSurfer, FSL-SIENAX and SPM brain volumetric measurements and the effect of lesion filling in multiple sclerosis.Eur Radiol. 2019 Mar;29(3):1355-1364. doi: 10.1007/s00330-018-5710-x. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Eur Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30242503 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of seed location on functional connectivity: evidence from an image-based meta-analysis.Front Neurosci. 2023 May 31;17:1120741. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1120741. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37325032 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bezdek JC, Hall LO, Clarke LP. Review of MRI Segmentation Techniques using Pattern Recognition. Med Phys. 1993;20:1033–48. - PubMed
-
- Held K, Rota Kops, Krause BJ, Wells WM, Kikinis R, Muller-Gartner HW. Markov random field segmentation of brain MR images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 1997;16:878–86. doi: 10.1109/42.650883. PubMed PMID: 9533587. - PubMed
-
- Liew A, Yan H. An Adaptive Spatial Fuzzy Clustering Algorithm for MR Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imag. 2003;22:1063–75. - PubMed
-
- Wells WM, Grimson WL, Kikinis R, Jolesz FA. Adaptive segmentation of MRI data. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 1996;15:429–42. doi: 10.1109/42.511747. PubMed PMID: 18215925. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
