Pleural fluid mesothelin as an adjunct to the diagnosis of pleural malignant mesothelioma
- PMID: 25505814
- PMCID: PMC4258360
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/413946
Pleural fluid mesothelin as an adjunct to the diagnosis of pleural malignant mesothelioma
Abstract
Rationale: The diagnosis of pleural malignant mesothelioma (MM) by effusion cytology may be difficult and is currently controversial. Effusion mesothelin levels are increased in patients with MM but the clinical role of this test is uncertain.
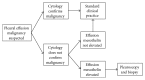
Objectives: To determine the clinical value of measuring mesothelin levels in pleural effusion supernatant to aid diagnosis of MM.
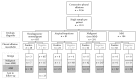
Methods and measurements: Pleural effusion samples were collected prospectively from 1331 consecutive patients. Mesothelin levels were determined by commercial ELISA in effusions and their relationship to concurrent pathology reporting and final clinical diagnosis was determined.
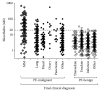
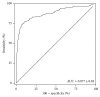
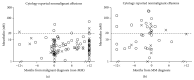
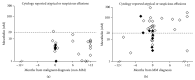
Results: 2156 pleural effusion samples from 1331 individuals were analysed. The final clinical diagnosis was 183 MM, 436 non-MM malignancy, and 712 nonmalignant effusions. Effusion mesothelin had a sensitivity of 67% for MM at 95% specificity. Mesothelin was elevated in over 47% of MM cases in effusions obtained before definitive diagnosis of MM was established. In the setting of inconclusive effusion cytology, effusion mesothelin had a positive predictive value of 79% for MM and 94% for malignancy.
Conclusions: A mesothelin-positive pleural effusion, irrespective of the identification of malignant cells, indicates the likely presence of malignancy and adds weight to the clinical rationale for further investigation to establish a malignant diagnosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hyaluronan and N-ERC/mesothelin as key biomarkers in a specific two-step model to predict pleural malignant mesothelioma.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 21;8(8):e72030. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072030. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23991032 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble mesothelin in effusions: a useful tool for the diagnosis of malignant mesothelioma.Thorax. 2007 Jul;62(7):569-76. doi: 10.1136/thx.2006.068114. Epub 2007 Mar 13. Thorax. 2007. PMID: 17356060 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of soluble mesothelin-related peptide as a diagnostic marker of malignant pleural mesothelioma effusions: its contribution to cytology.Cancer Invest. 2013 Jan;31(1):43-50. doi: 10.3109/07357907.2012.749265. Epub 2012 Dec 18. Cancer Invest. 2013. PMID: 23249166
-
Diagnostic value of soluble mesothelin-related peptides in pleural effusion for malignant pleural mesothelioma: An updated meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Apr;98(14):e14979. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014979. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 30946324 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of mesothelin and fibulin-3 in pleural fluid and serum as markers in malignant mesothelioma.Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2015 Jul;21(4):352-6. doi: 10.1097/MCP.0000000000000167. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2015. PMID: 26016578 Review.
Cited by
-
Scientific Advances and New Frontiers in Mesothelioma Therapeutics.J Thorac Oncol. 2018 Sep;13(9):1269-1283. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2018.06.011. J Thorac Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29966799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Malignant pleural effusion: from bench to bedside.Eur Respir Rev. 2016 Jun;25(140):189-98. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0019-2016. Eur Respir Rev. 2016. PMID: 27246596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA Signatures in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Effusions.Dis Markers. 2019 Jul 31;2019:8628612. doi: 10.1155/2019/8628612. eCollection 2019. Dis Markers. 2019. PMID: 31481984 Free PMC article.
-
Improved diagnosis and prognostication of patients with pleural malignant mesothelioma using biomarkers in pleural effusions and peripheral blood samples - a short report.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2017 Oct;40(5):511-519. doi: 10.1007/s13402-017-0327-7. Epub 2017 Jun 2. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2017. PMID: 28577209 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical utility of diagnostic biomarkers in malignant pleural mesothelioma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Respir Rev. 2021 Nov 17;30(162):210057. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0057-2021. Print 2021 Dec 31. Eur Respir Rev. 2021. PMID: 34789461 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Husain A. N., Colby T. V., Ordonez N. G., Krausz T., Borczuk A., Cagle P. T., Chirieac L. R., Churg A., Galateau-Salle F., Gibbs A. R., Gown A. M., Hammar S. P., Litzky L. A., Roggli V. L., Travis W. D., Wick M. R. Guidelines for pathologic diagnosis of malignant mesothelioma: a consensus statement from the International Mesothelioma Interest Group. Archives of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine. 2009;133(8):1317–1331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

