Histopathological Studies on Rabbits Infected by Bacteria Causing Infectious Keratitis in Human through Eye Inoculation
- PMID: 25505861
- PMCID: PMC4257361
- DOI: 10.12816/0023978
Histopathological Studies on Rabbits Infected by Bacteria Causing Infectious Keratitis in Human through Eye Inoculation
Abstract
Aim: This study aimed to investigate the pathogenic effect of bacteria causing infectious keratitis among patients through experimental study conducted on rabbits' eyes with the aid of histopathology as eye infection is a common disease in developing countries that may complicate to loss of vision.
Methodology: 100 swab samples were collected from human infected eyes, at Qassim region during 2012, for the isolation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. The isolated pathogenic bacteria were tested to various antibiotics using some selected antibiotics discs through agar-well diffusion method. Then, experimental study conducted on 27 rabbits. The rabbits were divided randomly into three equal groups, each containing 9 rabbits. Rabbits of group (1) served as control group (Negative Control) and their eyes were inoculated with the buffer only. Rabbits of group (2) were inoculated through eyes with the isolated Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rabbits of group (3) were inoculated through eyes with the isolated Staphylococcus aureus.
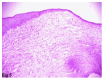
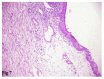
Results: Out of 100 collected swab samples from human infected eyes, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus were isolated with a total percentage of 25.21% and 15.65%; respectively and used in this study. Both bacterial isolates were sensitive to Gentamicin and Cefuroxime. Clinically, experimentally infected rabbits by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, revealed varying degree corneal abrasions, corneal abscess and dense corneal opacity. Histopathologically, at 3(rd) day post-infection (PI), the cornea revealed polymorpho-nuclear cells infiltration with loss of the outer epithelial lining. At 7(th) day PI, neutrophils were seen in the stroma. At 15(th) day PI, proliferation of fibroblasts and new vascularisation were seen in the stroma. Clinically, rabbits experimentally infected with Staphylococcus aureus, revealed corneal ulcers and focal abscesses. Histopathologically, at 3(rd) and 7(th) day PI, the cornea revealed edema and infiltration of leukocytes. At 15(th) day PI, hyperplasia of corneal epithelium and proliferation of keratocytes were evident. The liver and kidneys of experimented rabbits revealed no remarkable histopathological alterations along the period of experiment.
Conclusion: Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus are common eye infection in human, both induced severe lesions in the eyes of rabbits that could interfere with vision, therefore, strict measures to control these infections in human is recommended.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Increased susceptibility to infection in experimental xerophthalmia.Arch Ophthalmol. 1981 Sep;99(9):1614-7. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1981.03930020488019. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981. PMID: 6793031
-
Collagen cross-linking as monotherapy in experimentally induced corneal abscess in rabbits.BMC Ophthalmol. 2023 Jun 13;23(1):266. doi: 10.1186/s12886-023-03007-y. BMC Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37312088 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of ophthalmic gatifloxacin 0.3% and ciprofloxacin 0.3% in healing of corneal ulcers associated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced ulcerative keratitis in rabbits.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2005 Feb;21(1):36-43. doi: 10.1089/jop.2005.21.36. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2005. PMID: 15718826
-
Comparison between corneal cross-linking, topical antibiotic and combined therapy in experimental bacterial keratitis model.Saudi J Ophthalmol. 2018 Apr-Jun;32(2):97-104. doi: 10.1016/j.sjopt.2017.10.003. Epub 2017 Oct 28. Saudi J Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 29942176 Free PMC article.
-
Corneal Involvement in HIV-infected Individuals.Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2021 Aug 18;29(6):1177-1182. doi: 10.1080/09273948.2021.1887283. Epub 2021 Jul 7. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2021. PMID: 34232799 Review.
Cited by
-
Repair Process Impairment by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Epithelial Tissues: Major Features and Potential Therapeutic Avenues.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 May 31;9:182. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00182. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31214514 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Diesem C. The Anatomy of the Domestic Animals. W.G. Saunders Company; Philadelphia, London, Toronto, Mexico City, Rode Janise, Sydney, Tokyo: 1975. Sense organ and common integuments. Revised by R Getty.
-
- Dellmann HD, Collier LL. Eye. In: Dellmann HD, Brown EM, editors. Textbook of Veterinary Histology. 3rd ed. Lea & Febiger; Philadelphia: 1987. pp. 416–433.
-
- Banks WJ. Applied Veterinary Histology. 3rd ed. Mosby Year Book; St. Louis, Baltimore, Boston, Chicago, London, Philadelphia, Sydney, Toronto: 1993.
-
- Slatter D. Fundamentals of veterinary ophthalmology. 3rd ed. W.B. Saunders Company; Philadelphia, London, New York, St. Louis, Sydney, Toronto: 2001. Structure and function of the eye.
-
- Patt DI, Patt GR. Comparative Vertebrate Histology: Harper & Row Publishers; New York, Evanston, London: 1969. pp. 372–391.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
