The neuron-astrocyte-microglia triad in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion: protective effect of dipyridamole
- PMID: 25505884
- PMCID: PMC4245920
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2014.00322
The neuron-astrocyte-microglia triad in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion: protective effect of dipyridamole
Abstract
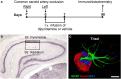
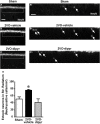
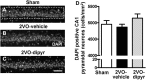
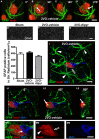
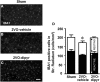
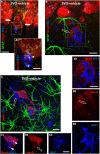
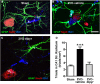
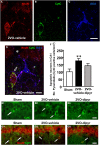
Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion during aging may cause progressive neurodegeneration as ischemic conditions persist. Proper functioning of the interplay between neurons and glia is fundamental for the functional organization of the brain. The aim of our research was to study the pathophysiological mechanisms, and particularly the derangement of the interplay between neurons and astrocytes-microglia with the formation of "triads," in a model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induced by the two-vessel occlusion (2VO) in adult Wistar rats (n = 15). The protective effect of dipyridamole given during the early phases after 2VO (4 mg/kg/day i.v., the first 7 days after 2VO) was verified (n = 15). Sham-operated rats (n = 15) were used as controls. Immunofluorescent triple staining of neurons (NeuN), astrocytes (GFAP), and microglia (IBA1) was performed 90 days after 2VO. We found significantly higher amount of "ectopic" neurons, neuronal debris and apoptotic neurons in CA1 Str. Radiatum and Str. Pyramidale of 2VO rats. In CA1 Str. Radiatum of 2VO rats the amount of astrocytes (cells/mm(2)) did not increase. In some instances several astrocytes surrounded ectopic neurons and formed a "micro scar" around them. Astrocyte branches could infiltrate the cell body of ectopic neurons, and, together with activated microglia cells formed the "triads." In the triad, significantly more numerous in CA1 Str. Radiatum of 2VO than in sham rats, astrocytes and microglia cooperated in the phagocytosis of ectopic neurons. These events might be common mechanisms underlying many neurodegenerative processes. The frequency to which they appear might depend upon, or might be the cause of, the burden and severity of neurodegeneration. Dypiridamole significantly reverted all the above described events. The protective effect of chronic administration of dipyridamole might be a consequence of its vasodilatory, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory role during the early phases after 2VO.
Keywords: CA1; apoptosis; confocal microscopy; neuron-astrocyte-microglia triad; phagocytosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The neuron-astrocyte-microglia triad in CA3 after chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in the rat: Protective effect of dipyridamole.Exp Gerontol. 2017 Oct 1;96:46-62. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2017.06.006. Epub 2017 Jun 9. Exp Gerontol. 2017. PMID: 28606482
-
The neuron-astrocyte-microglia triad involvement in neuroinflammaging mechanisms in the CA3 hippocampus of memory-impaired aged rats.Exp Gerontol. 2016 Oct;83:71-88. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2016.07.011. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Exp Gerontol. 2016. PMID: 27466072
-
An Overview on the Differential Interplay Among Neurons-Astrocytes-Microglia in CA1 and CA3 Hippocampus in Hypoxia/Ischemia.Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Nov 11;14:585833. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.585833. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33262692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The neuron-astrocyte-microglia triad in normal brain ageing and in a model of neuroinflammation in the rat hippocampus.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45250. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045250. Epub 2012 Sep 18. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23028880 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Role of the Interplay Among Astrocytes, Microglia, and Neurons in the Hippocampus in Health and Disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Apr 6;13:651973. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.651973. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33889084 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anticonvulsant Action and Long-Term Effects of Chronic Cannabidiol Treatment in the Rat Pentylenetetrazole-Kindling Model of Epilepsy.Biomedicines. 2022 Jul 28;10(8):1811. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10081811. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36009358 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of two-stage carotid occlusion on spatial memory and pro-inflammatory markers in the hippocampus of rats.J Physiol Sci. 2017 May;67(3):415-423. doi: 10.1007/s12576-016-0474-z. Epub 2016 Jul 28. J Physiol Sci. 2017. PMID: 27470129 Free PMC article.
-
Review of Alzheimer's disease drugs and their relationship with neuron-glia interaction.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2022 Nov 19;14:64-76. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2022.11.005. eCollection 2023 Jun. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36593897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress of mitophagy in chronic cerebral ischemia.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Aug 3;15:1224633. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1224633. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37600521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Selective Antagonism of Adenosine A2B Receptors Reduces the Synaptic Failure and Neuronal Death Induced by Oxygen and Glucose Deprivation in Rat CA1 Hippocampus in Vitro.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Apr 24;9:399. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00399. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29740323 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

