Conditioned Medium Reconditions Hippocampal Neurons against Kainic Acid Induced Excitotoxicity: An In Vitro Study
- PMID: 25505907
- PMCID: PMC4258312
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/194967
Conditioned Medium Reconditions Hippocampal Neurons against Kainic Acid Induced Excitotoxicity: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
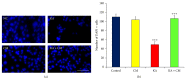
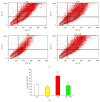
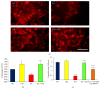
Stem cell therapy is gaining attention as a promising treatment option for neurodegenerative diseases. The functional efficacy of grafted cells is a matter of debate and the recent consensus is that the cellular and functional recoveries might be due to "by-stander" effects of grafted cells. In the present study, we investigated the neuroprotective effect of conditioned medium (CM) derived from human embryonic kidney (HEK) cells in a kainic acid (KA) induced hippocampal degeneration model system in in vitro condition. Hippocampal cell line was exposed to KA (200 µM) for 24 hrs (lesion group) whereas, in the treatment group, hippocampal cell line was exposed to KA in combination with HEK-CM (KA + HEK-CM). We observed that KA exposure to cells resulted in significant neuronal loss. Interestingly, HEK-CM cotreatment completely attenuated the excitotoxic effects of KA. In HEK-CM cotreatment group, the cell viability was ~85-95% as opposed to 47% in KA alone group. Further investigation demonstrated that treatment with HEK-CM stimulated the endogenous cell survival factors like brain derived neurotrophic factors (BDNF) and antiapoptotic factor Bcl-2, revealing the possible mechanism of neuroprotection. Our results suggest that HEK-CM protects hippocampal neurons against excitotoxicity by stimulating the host's endogenous cell survival mechanisms.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Infusion of human embryonic kidney cell line conditioned medium reverses kainic acid induced hippocampal damage in mice.Cytotherapy. 2014 Dec;16(12):1760-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2014.07.001. Epub 2014 Oct 22. Cytotherapy. 2014. PMID: 25442789
-
HEK-293 secretome attenuates kainic acid neurotoxicity through insulin like growth factor-phosphatidylinositol-3-kinases pathway and by temporal regulation of antioxidant defense machineries.Neurotoxicology. 2018 Dec;69:189-200. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2017.11.010. Epub 2017 Dec 6. Neurotoxicology. 2018. PMID: 29208536
-
Neuroprotective effects of a protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor against hippocampal excitotoxic injury.Brain Res. 2019 Sep 15;1719:133-139. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2019.05.027. Epub 2019 May 22. Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 31128098
-
Kainic acid-mediated excitotoxicity as a model for neurodegeneration.Mol Neurobiol. 2005;31(1-3):3-16. doi: 10.1385/MN:31:1-3:003. Mol Neurobiol. 2005. PMID: 15953808 Review.
-
Adiponectin protects hippocampal neurons against kainic acid-induced excitotoxicity.Brain Res Rev. 2009 Oct;61(2):81-8. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2009.05.002. Epub 2009 May 19. Brain Res Rev. 2009. PMID: 19460404 Review.
Cited by
-
Trkb-IP3 Pathway Mediating Neuroprotection in Rat Hippocampal Neuronal Cell Culture Following Induction of Kainic Acid.Malays J Med Sci. 2018 Nov;25(6):28-45. doi: 10.21315/mjms2018.25.6.4. Epub 2018 Dec 28. Malays J Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30914877 Free PMC article.
-
Conditioned medium of E17 rat brain cells induced differentiation of primary colony of mice blastocyst into neuron-like cells.J Vet Sci. 2021 Nov;22(6):e86. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2021.22.e86. J Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 34854268 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shaw P. J. Excitatory amino acid neurotransmission, excitotoxicity and excitotoxins. Current Opinion in Neurology and Neurosurgery. 1992;5(3):383–390. - PubMed
-
- Rekha J., Chakravarthy S., Veena L. R., Kalai V. P., Choudhury R., Halahalli H. N., Alladi P. A., Dhanushkodi A., Nirmala M., Swamilingiah G. M., Agrahari M., Raju T. R., Panicker M. M., Kutty B. M. Transplantation of hippocampal cell lines restore spatial learning in rats with ventral subicular lesions. Behavioral Neuroscience. 2009;123(6):1197–1217. doi: 10.1037/a0017655. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rekha J., Veena L. R., Prem N., Kalaivani P., Choudhury R., Alladi P. A., Agrahari M., Raju T. R., Kutty B. M. NIH-3T3 fibroblast transplants enhance host regeneration and improve spatial learning in ventral subicular lesioned rats. Behavioural Brain Research. 2011;218(2):315–324. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2010.11.020. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

