Molecular-cytogenetic analysis of Aegilops triuncialis and identification of its chromosomes in the background of wheat
- PMID: 25505933
- PMCID: PMC4263106
- DOI: 10.1186/s13039-014-0091-6
Molecular-cytogenetic analysis of Aegilops triuncialis and identification of its chromosomes in the background of wheat
Abstract
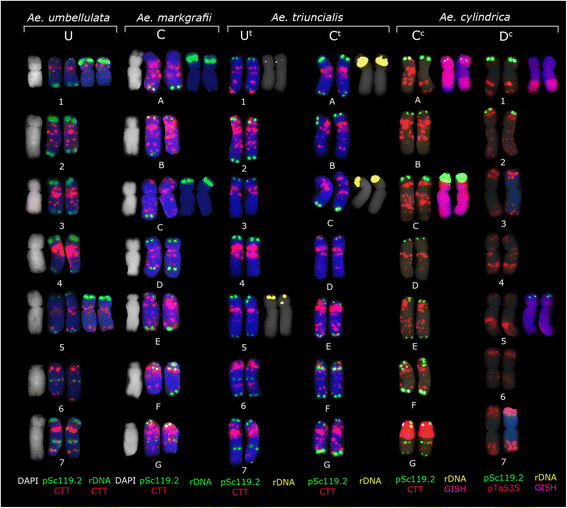
Background: Species belonging to the genus Aegilops L. are an important source of genetic material for expanding genetic variability of wheat. Ae. triuncialis is an allotetraploid in this genus which was originated from hybridization of Ae. umbellulata and Ae. markgrafii (Greuter) Hammer. Although the Ae. triuncialis karyotype was thoroughly examined by conventional chromosome staining and Giemsa C-banding, it is still poorly characterized using FISH markers. The objective of this study was to test the fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) patterns of Ae. triuncialis (2n = 4x = 28, C(t)C(t)U(t)U(t)) chromosomes using different repetitive sequences and to compare the produced patterns to the chromosomes of its diploid ancestors, with the aim of establishing a generalized Ae. triuncialis idiogram and detection of Aegilops chromosomes in the background of wheat.
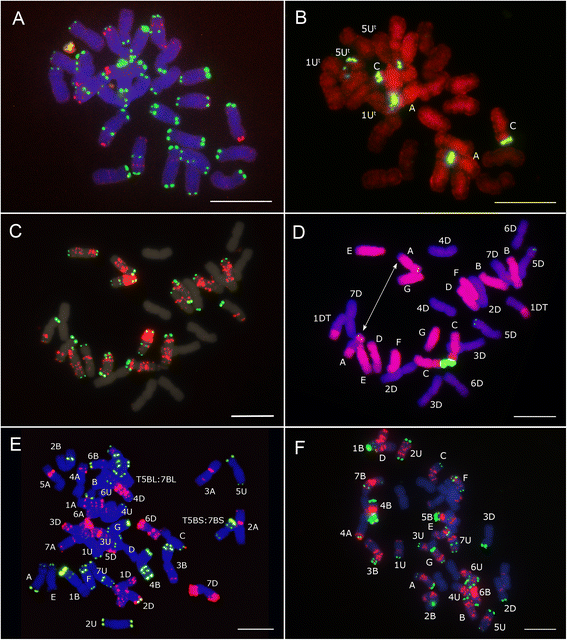
Results: The probes pSc119.2-1, pTa535-1, pAs1-1, (CTT)10 and the 45S rDNA clone from wheat (pTa71) were hybridized to chromosomes of Ae. triuncialis and compared with its diploid progenitors (Ae. umbellulata Zhuk., 2n = 2x = 14, UU and Ae. markgrafii (Greuter) Hammer, 2n = 2x = 14, CC) and Ae. cylindrica Host. (2n = 4x = 28, D(c)D(c)C(c)C(c)), another tetraploid species containing the C-genome. Ae. cylindrica was further analyzed by genomic in situ hybridization (GISH) using C genome probe in order to identify any possible translocation.
Conclusions: In general, FISH patterns of the U(t)- and C(t)-genome chromosomes of Ae. triuncialis were similar to those of U- and C-genome chromosomes of the diploid progenitor species Ae. umbellulata and Ae. markgrafii respectively, although some differences were observed. Two major 45S rDNA loci were revealed in the short arm of chromosomes A and C, of the C(t) genome which correspond to homoeologous groups 1 and 5 respectively. Minor 45S rDNA loci were mapped on the short arm of chromosomes 1U(t) and 5U(t). GISH analysis revealed three different non-reciprocal homologous or heterologous translocations between C(c) and D(c) chromosomes in all studied accessions of Ae. cylindrica.
Keywords: Aegilops triuncialis; Allopolyploidization; Chromosome marker; Evolution; Wheat–Aegilops triuncialis hybrid.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Flow sorting of C-genome chromosomes from wild relatives of wheat Aegilops markgrafii, Ae. triuncialis and Ae. cylindrica, and their molecular organization.Ann Bot. 2015 Aug;116(2):189-200. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcv073. Epub 2015 Jun 4. Ann Bot. 2015. PMID: 26043745 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular cytogenetic characterization of Aegilops biuncialis and its use for the identification of 5 derived wheat-Aegilops biuncialis disomic addition lines.Genome. 2005 Dec;48(6):1070-82. doi: 10.1139/g05-062. Genome. 2005. PMID: 16391676
-
Dynamic nucleolar activity in wheat × Aegilops hybrids: evidence of C-genome dominance.Plant Cell Rep. 2017 Aug;36(8):1277-1285. doi: 10.1007/s00299-017-2152-x. Epub 2017 Apr 29. Plant Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28456843
-
Broadening the bread wheat D genome.Theor Appl Genet. 2019 May;132(5):1295-1307. doi: 10.1007/s00122-019-03299-z. Epub 2019 Feb 10. Theor Appl Genet. 2019. PMID: 30739154 Review.
-
Gametocidal genes of Aegilops: segregation distorters in wheat-Aegilops wide hybridization.Genome. 2017 Aug;60(8):639-647. doi: 10.1139/gen-2017-0023. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Genome. 2017. PMID: 28654760 Review.
Cited by
-
The Polymorphisms of Oligonucleotide Probes in Wheat Cultivars Determined by ND-FISH.Molecules. 2019 Mar 21;24(6):1126. doi: 10.3390/molecules24061126. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30901897 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Structural Genomic Diversity in Aegilops umbellulata, Ae. markgrafii, Ae. comosa, and Ae. uniaristata by Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization Karyotyping.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Jun 9;11:710. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00710. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32655588 Free PMC article.
-
Oligonucleotides and ND-FISH Displaying Different Arrangements of Tandem Repeats and Identification of Dasypyrum villosum Chromosomes in Wheat Backgrounds.Molecules. 2017 Jun 14;22(6):973. doi: 10.3390/molecules22060973. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28613230 Free PMC article.
-
Physical location of tandem repeats in the wheat genome and application for chromosome identification.Planta. 2019 Mar;249(3):663-675. doi: 10.1007/s00425-018-3033-4. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Planta. 2019. PMID: 30357506
-
Evolution of the S-Genomes in Triticum-Aegilops Alliance: Evidences From Chromosome Analysis.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Dec 4;9:1756. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01756. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 30564254 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schneider A, Molnár I, Molnár-Láng M. Utilisation of Aegilops (goatgrass) species to widen the genetic diversity of cultivated wheat. Euphytica. 2008;163:1–19. doi: 10.1007/s10681-007-9624-y. - DOI
-
- Van Slageren MW. Wild Wheats: a monograph of Aegilops L. and Amblyopyrum (Jaub. et Spach) Eig (Poaceae) Wageningen Agricultural University, Wageningen and ICARDA, Aleppo, Syria: Wageningen; 1994.
-
- Kimber G, Tsunewaki K. Genome symbols and plasma types in the wheat group. In: Miller TE, Koebner RMD, editors. Proceedings of the 7th International Wheat Genetics Symposium, 13–19 July 1988. Cambridge, England: Institute of Plant Science Research, Cambridge Laboratory, Trumpington, England; 1996. pp. 1209–1210.
-
- Murai K, Tsunewaki K. Molecular basis of genetic diversity among cytoplasms of Triticum and Aegilops species. IV. CtDNA variation in Ae. triuncialis. Heredity. 1986;57:335–339. doi: 10.1038/hdy.1986.132. - DOI
-
- Vanichanon A, Blake N, Sherman J, Talbert L. Multiple origins of allopolyploid Aegilops triuncialis. Theor Appl Genet. 2003;106:804–810. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

