Invariant natural killer T-cell neutralization is a possible novel therapy for human eosinophilic esophagitis
- PMID: 25505954
- PMCID: PMC4232063
- DOI: 10.1038/cti.2013.13
Invariant natural killer T-cell neutralization is a possible novel therapy for human eosinophilic esophagitis
Abstract
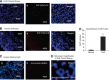
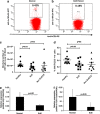
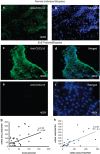
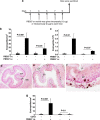
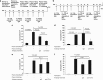
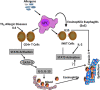
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a recently recognized inflammatory disorder that needs a potential therapeutic strategy. We earlier showed that iNKT cell-deficient mice are protected from allergen-induced EoE. Therefore, we now tested the hypothesis that iNKT cells are induced in the human EoE and is a novel possible target for the treatment of human EoE. Accordingly, we examine number of iNKT cells and eosinophils and expression of iNKT-associated cell surface receptors and chemokines by performing immunofluorescence, qPCR and ELISA in the esophageal biopsies and blood samples of normal subjects (comparison control) and EoE patients. Herein, we show that iNKT cell number, their receptor subcomponents Vα24 and Vβ11 expression, and associated chemokine CXCL16 levels (or expression) are induced significantly in EoE patients compared with normal individuals. In addition, we show that CXCL16 levels (or expression) correlate with the mRNA levels of Vα24 receptor but not well with esophageal eosinophilia in human EoE. Of note, we show that in vivo activation of iNKT cells is sufficient to induce EoE in mice. Furthermore, we show that anti-mCD1d- and anti-hVα24Jα18-neutralizing antibody treatment protects allergen-induced experimental EoE. Taken together, we have shown first time that iNKT cells have a critical pathogenic role in human and experimental EoE. iNKT cell neutralization by humanized anti-CD1d and anti-Vα24Jα18 antibodies might be a novel and potential therapy for human EoE.
Keywords: CXCL16; PBS57; anti-CD1d; anti-Vα24Jα18; iNKT cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Involvement of the iNKT cell pathway is associated with early-onset eosinophilic esophagitis and response to allergen avoidance therapy.Am J Gastroenterol. 2014 May;109(5):646-57. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2014.12. Epub 2014 Feb 11. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24513807 Free PMC article.
-
Allergen-induced interleukin-18 promotes experimental eosinophilic oesophagitis in mice.Immunol Cell Biol. 2015 Nov;93(10):849-57. doi: 10.1038/icb.2015.30. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Immunol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25801352 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of para-esophageal lymph nodes in food or aeroallergen-induced iNKT cell-mediated experimental eosinophilic esophagitis.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012 Apr;302(7):G645-54. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00223.2011. Epub 2011 Dec 29. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22207581 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Applications of the Eosinophilic Esophagitis Diagnostic Panel.Front Med (Lausanne). 2017 Jul 14;4:108. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2017.00108. eCollection 2017. Front Med (Lausanne). 2017. PMID: 28770203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological Therapies for Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Where Do We Stand?Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018 Oct;55(2):205-216. doi: 10.1007/s12016-018-8674-3. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29372536 Review.
Cited by
-
Intestinal overexpression of interleukin (IL)-15 promotes tissue eosinophilia and goblet cell hyperplasia.Immunol Cell Biol. 2018 Mar;96(3):273-283. doi: 10.1111/imcb.1036. Epub 2017 Dec 29. Immunol Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29363170 Free PMC article.
-
Signals from the various immune cells in promoting food allergy-induced eosinophilic esophagitis like disease.Asia Pac Allergy. 2019 Jul 31;9(3):e28. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2019.9.e28. eCollection 2019 Jul. Asia Pac Allergy. 2019. PMID: 31384583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Allergic mechanisms of Eosinophilic oesophagitis.Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2015 Oct;29(5):709-720. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2015.09.012. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26552770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of Severe Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Multi-Organ Inflammation by Airborne Allergens is Associated with IL-4/IL-13 and CCL11 but Not IgE in Genetic Susceptible Mice.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Sep 23;15:5527-5540. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S372449. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 36176352 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacotherapies for the Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: State of the Art Review.Drugs. 2019 Sep;79(13):1419-1434. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-01173-2. Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31352605 Review.
References
-
- Noel RJ, Putnam PE, Collins MH, Assa'ad AH, Guajardo JR, Jameson SC, et al. Clinical and immunopathologic effects of swallowed fluticasone for eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004;2:568–575. - PubMed
-
- Rothenberg ME. Eosinophilia. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1592–1600. - PubMed
-
- Rothenberg ME. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGID) J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;113:11–28. - PubMed
-
- Mishra A, Rothenberg ME. Intratracheal IL-13 induces eosinophilic esophagitis by an IL-5, eotaxin-1, and STAT6-dependent mechanism. Gastroenterology. 2003;125:1419–1427. - PubMed
-
- Akei HS, Mishra A, Blanchard C, Rothenberg ME. Epicutaneous antigen exposure primes for experimental eosinophilic esophagitis in mice. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:985–994. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
