Clinical immune-monitoring strategies for predicting infection risk in solid organ transplantation
- PMID: 25505960
- PMCID: PMC4232060
- DOI: 10.1038/cti.2014.3
Clinical immune-monitoring strategies for predicting infection risk in solid organ transplantation
Abstract
Infectious complications remain a leading cause of morbidity and mortality after solid organ transplantation (SOT), and largely depend on the net state of immunosuppression achieved with current regimens. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a major opportunistic viral pathogen in this setting. The application of strategies of immunological monitoring in SOT recipients would allow tailoring of immunosuppression and prophylaxis practices according to the individual's actual risk of infection. Immune monitoring may be pathogen-specific or nonspecific. Nonspecific immune monitoring may rely on either the quantification of peripheral blood biomarkers that reflect the status of a given arm of the immune response (serum immunoglobulins and complement factors, lymphocyte sub-populations, soluble form of CD30), or on the functional assessment of T-cell responsiveness (release of intracellular adenosine triphosphate following a mitogenic stimulus). In addition, various methods are currently available for monitoring pathogen-specific responses, such as CMV-specific T-cell-mediated immune response, based on interferon-γ release assays, intracellular cytokine staining or main histocompatibility complex-tetramer technology. This review summarizes the clinical evidence to date supporting the use of these approaches to the post-transplant immune status, as well as their potential limitations. Intervention studies based on validated strategies for immune monitoring still need to be performed.
Keywords: cell-mediated immunity; cytomegalovirus; immune-monitoring strategies; infection; prediction; solid organ transplantation.
Figures

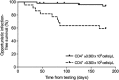
References
-
- Fishman JA, Issa NC. Infection in organ transplantation: risk factors and evolving patterns of infection. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2010;24:273–283. - PubMed
-
- Fishman JA, AST Infectious Diseases Community of Practice Introduction: infection in solid organ transplant recipients. Am J Transplant. 2009;9 (Suppl 4:S3–S6. - PubMed
-
- Kuypers DR. Immunosuppressive drug monitoring—what to use in clinical practice today to improve renal graft outcome. Transpl Int. 2005;18:140–150. - PubMed
-
- Fleming JN, Weimert NA. Novel strategies for immune monitoring in kidney transplant recipients. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2010;17:e63–e77. - PubMed
-
- Kuypers DR, Le Meur Y, Cantarovich M, Tredger MJ, Tett SE, Cattaneo D, et al. Consensus report on therapeutic drug monitoring of mycophenolic acid in solid organ transplantation. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;5:341–358. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
