Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infection Occurring after Exposure to Mycobacterium marinum
- PMID: 25506004
- PMCID: PMC4254079
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/702613
Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infection Occurring after Exposure to Mycobacterium marinum
Abstract
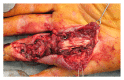
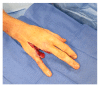
Cutaneous infections caused by Mycobacterium marinum have been attributed to aquarium or fish exposure after a break in the skin barrier. In most instances, the upper limbs and fingers account for a majority of the infection sites. While previous cases of necrotizing soft tissue infections related to M. marinum have been documented, the importance of our presenting case is to illustrate the aggressive nature of M. marinum resulting in a persistent necrotizing soft tissue infection of a finger that required multiple aggressive wound debridements, followed by an amputation of the affected extremity, in order to hasten recovery.
Figures


References
-
- Johnson R. P., Xia Y., Cho S., Burroughs R. F., Krivda S. J. Mycobacterium marinum infection: a case report and review of the literature. Cutis. 2007;79(1):33–36. - PubMed
-
- Dolenc-Voljc M., Zolnir-Dovc M. Delayed diagnosis of Mycobacterium marinum infection: a case report and review of the literature. Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica, et Adriatica. 2010;19(2):35–39. - PubMed
-
- Kumar A. R., Grewal N. S., Katchikian H. V., Jones N. F. Complex Mycobacterium marinum hand infections: case reports and review of literature. Infectious Diseases in Clinical Practice. 2008;16(5):278–282. doi: 10.1097/IPC.0b013e3181778886. - DOI
-
- Van Seymortier P., Verellen K., De Jonge I. Mycobacterium marinum causing tenosynovitis. ‘Fish tank finger’. Acta Orthopaedica Belgica. 2004;70(3):279–282. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

