Hormonal treatment for severe hydronephrosis caused by bladder endometriosis
- PMID: 25506035
- PMCID: PMC4251884
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/891295
Hormonal treatment for severe hydronephrosis caused by bladder endometriosis
Abstract
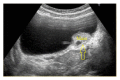
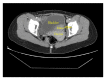
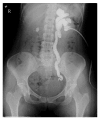
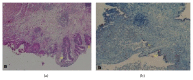
The incidence of endometriosis cases involving the urinary system has recently increased, and the bladder is a specific zone where endometriosis is most commonly seen in the urinary system. In the case presented here, a patient presented to the emergency department with the complaint of side pain and was examined and diagnosed with severe hydronephrosis and bladder endometriosis was determined in the etiology. After the patient was pathologically diagnosed, Levonorgestrel-Releasing Intrauterine System (LNG-IUS) was administered to the uterine cavity. At the 12-month follow-up, endometriosis was not observed in the cystoscopy and symptoms had completely regressed. Hydronephrosis may be observed after exposure of the ureter, and silent renal function loss may develop in patients suffering from endometriosis with bladder involvement. For patients with moderate or severe hydronephrosis associated with bladder endometriosis, LNG-IUS application may be separately and successfully used after conservative surgery.
Figures
References
-
- Luscombe G. M., Markham R., Judio M., Grigoriu A., Fraser I. S. Abdominal bloating: an under-recognized endometriosis symptom. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada. 2009;31(12):1159–1171. - PubMed
-
- Chapron C., Fauconnier A., Vieira M., Barakat H., Dousset B., Pansini V., Vacher-Lavenu M. C., Dubuisson J. B. Anatomical distribution of deeply infiltrating endometriosis: surgical implications and proposition for a classification. Human Reproduction. 2003;18(1):157–161. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deg009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nezhat C., Nezhat F., Nezhat C. H., Nasserbakht F., Rosati M., Seidman D. S. Urinary tract endometriosis treated by laparoscopy. Fertility and Sterility. 1996;66(6):920–924. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

