Efficacy and tolerability of Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761® in dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials
- PMID: 25506211
- PMCID: PMC4259871
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S72728
Efficacy and tolerability of Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761® in dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials
Abstract
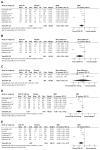
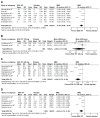
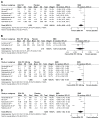
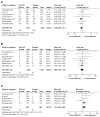
The objective of this systematic review was to evaluate current evidence for the efficacy of Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761(®) in dementia. Seven of 15 randomized, placebo-controlled trials in patients with dementia identified by database searches met all our selection criteria and were included in the meta-analysis. In these trials, patients were treated with 120 mg or 240 mg per day of the defined extract EGb 761 or placebo. Efficacy was assessed using validated tests and rating scales for the cognitive domain, the functional domain (activities of daily living), and global assessment. Tolerability was evaluated by risk differences based on incidences of adverse events and premature discontinuation rates. Of 2,684 outpatients randomized to receive treatment for 22-26 weeks, 2,625 represented the full analysis sets (1,396 for EGb 761 and 1,229 for placebo). Standardized mean differences for change in cognition (-0.52; 95% confidence interval [CI] -0.98, -0.05; P=0.03), activities of daily living (-0.44; 95% CI -0.68, -0.19; P<0.001), and global rating (-0.52; 95% CI -0.92, -0.12; P=0.01) significantly favored EGb 761 compared with placebo. Statistically significant superiority of EGb 761 over placebo was confirmed by responder analyses as well as for patients suffering from dementia with neuropsychiatric symptoms. Treatment-associated risks in terms of relative risks of adverse events and premature withdrawal rates did not differ noticeably between the two treatment groups. In conclusion, meta-analyses confirmed the efficacy and good tolerability of Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761 in patients with dementia.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; efficacy; mixed dementia; safety; vascular dementia.
Figures

References
-
- Schneider JA, Arvanitakis Z, Bang W, Bennett DA. Mixed brain pathologies account for most dementia cases in community-dwelling older persons. Neurology. 2007;69(24):2197–2204. - PubMed
-
- Ihl R, Frölich L, Winblad B, Schneider L, Burns A, Möller HJ WFSBP Task Force on Treatment Guidelines for Alzheimer’s Disease and other Dementias. World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) guidelines for the biological treatment of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2011;12(1):2–32. - PubMed
-
- Abdel-Kader R, Hauptmann S, Keil U, et al. Stabilization of mitochondrial function by Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761®) Pharmacol Res. 2007;56(6):493–502. - PubMed
-
- Tchantchou F, Xu Y, Wu Y, Christen Y, Luo Y. EGb 761® enhances adult hippocampal neurogenesis and phosphorylation of CREB in transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. FASEB J. 2007;21(10):2400–2408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

