Olive oil in the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis after artificial menopause
- PMID: 25506212
- PMCID: PMC4259560
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S72006
Olive oil in the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis after artificial menopause
Abstract
Purpose: The goal of this study was to investigate the anti-osteoporosis effect of extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) in vivo, and explore its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory properties in Sprague Dawley rats and its anticancer properties in patients.
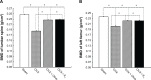
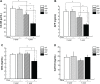
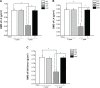
Materials and methods: A total of 120 healthy female Sprague Dawley rats aged 6 months were divided into four groups: 1) sham-operated control (Sham group, n=30); 2) ovariectomized (OVX group, n=30); 3) ovariectomized rats supplemented with EVOO (OVX + Olive, n=30); 4) ovariectomized rats supplemented with estrogen (OVX + E2, n=30). EVOO and estrogen were administered by oral gavage at a dose of 1 mL/100 g weight on a daily basis for 12 consecutive weeks. Twelve weeks later blood samples were obtained to detect the levels of calcium, alkaline phosphatase, phosphorus, interleukin-6 (IL-6), malonyldialdehyde (MDA), and nitrate content. Dual energy X-ray absorptiometer measured bone mineral density (BMD) of ovariectomized Sprague Dawley rats that had been fed olive oil for 3 months. Blood samples from patients, who regularly consumed olive oil over a 1 year period were also used to measure carbohydrate antigen 125, carcino-embryonic antigen, α-fetoprotein, and carbohydrate antigen 19-9 levels. BMD of lumbar spine and left femur was also evaluated by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry.
Results: Animal experiments showed that EVOO significantly increased BMD and decreased phosphatase, alkaline phosphatase, IL-6, MDA, and nitrate levels. However, it had no significant effect on the Ca(2+) level. In clinical follow-up, EVOO also improved patient BMD levels on L3, L4, and left femoral neck, and reduced carbohydrate antigen 125, α-fetoprotein, and carcino-embryonic antigen levels. But it had no significant effect on the carbohydrate antigen 19-9 level.
Conclusion: EVOO illustrated significant anti-osteoporosis, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties in vivo. However, further studies are required to determine the active component(s) responsible for these effects.
Keywords: artificial menopause; olive oil; osteoporosis; prevention; treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Lyman GH, Khorana AA, Kuderer NM, et al. Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis and treatment in patients with cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(17):2189–2204. - PubMed
-
- Puel C, Mardon J, Kati-Coulibaly S, et al. Black Lucques olives prevented bone loss caused by ovariectomy and talc granulomatosis in rats. Br J Nutr. 2007;97(5):1012–1020. - PubMed
-
- Ershler WB, Harman SM, Keller ET. Immunologic aspects of osteoporosis. Dev Comp Immunol. 1997;21(6):487–499. - PubMed
-
- Valls RM, Farras M, Suarez M, et al. Effects of functional olive oil enriched with its own phenolic compounds on endothelial function in hypertensive patients. A randomised controlled trial. Food Chem. 2015;167:30–35. - PubMed
-
- Stevenson JC, Panay N, Pexman-Fieth C. Corrigendum to Oral estradiol and dydrogesterone combination therapy in postmenopausal women: Review of efficacy and safety. Maturitas. 2013;76(4):388. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

