The process of EDC-NHS Cross-linking of reconstituted collagen fibres increases collagen fibrillar order and alignment
- PMID: 25506518
- PMCID: PMC4262854
- DOI: 10.1063/1.4900887
The process of EDC-NHS Cross-linking of reconstituted collagen fibres increases collagen fibrillar order and alignment
Abstract
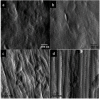
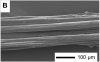
We describe the production of collagen fibre bundles through a multi-strand, semi-continuous extrusion process. Cross-linking using an EDC (1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide), NHS (N-hydroxysuccinimide) combination was considered. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) and Raman spectroscopy focused on how cross-linking affected the collagen fibrillar structure. In the cross-linked fibres, a clear fibrillar structure comparable to native collagen was observed which was not observed in the non-cross-linked fibre. The amide III doublet in the Raman spectra provided additional evidence of alignment in the cross-linked fibres. Raman spectroscopy also indicated no residual polyethylene glycol (from the fibre forming buffer) or water in any of the fibres.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide and N-hydroxysuccinimide concentrations on the mechanical and biological characteristics of cross-linked collagen fibres for tendon repair.Regen Biomater. 2015 Jun;2(2):77-85. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbv005. Epub 2015 May 16. Regen Biomater. 2015. PMID: 26816633 Free PMC article.
-
The structural analysis of three-dimensional fibrous collagen hydrogels by Raman microspectroscopy.Biopolymers. 2013 Jun;99(6):349-56. doi: 10.1002/bip.22183. Biopolymers. 2013. PMID: 23529687
-
A comparative study on cross-linking of fibrillar gel prepared by tilapia collagen and hyaluronic acid with EDC/NHS and genipin.Int J Biol Macromol. 2022 Jul 31;213:639-650. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.06.006. Epub 2022 Jun 4. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022. PMID: 35671907
-
Extruded collagen fibres for tissue engineering applications: effect of crosslinking method on mechanical and biological properties.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2011 Jun;22(6):1569-78. doi: 10.1007/s10856-011-4336-1. Epub 2011 May 10. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2011. PMID: 21556975
-
Cross-linking by 1-ethyl-3- (3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide (EDC) of a collagen/elastin membrane meant to be used as a dermal substitute: effects on physical, biochemical and biological features in vitro.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2001 May;12(5):437-46. doi: 10.1023/a:1011205221972. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2001. PMID: 15348284
Cited by
-
3D Printing of Organs-On-Chips.Bioengineering (Basel). 2017 Jan 25;4(1):10. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering4010010. Bioengineering (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28952489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization and Biological Evaluation of Composite Nanofibrous Membranes Prepared from Hemp Salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) Skin Collagen.Cells. 2025 Apr 3;14(7):537. doi: 10.3390/cells14070537. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40214490 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide and N-hydroxysuccinimide concentrations on the mechanical and biological characteristics of cross-linked collagen fibres for tendon repair.Regen Biomater. 2015 Jun;2(2):77-85. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbv005. Epub 2015 May 16. Regen Biomater. 2015. PMID: 26816633 Free PMC article.
-
Manufacture and characterisation of EmDerm-novel hierarchically structured bio-active scaffolds for tissue regeneration.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2018 Jun 5;29(6):79. doi: 10.1007/s10856-018-6060-6. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2018. PMID: 29872930 Free PMC article.
-
Cobalt/Bioglass Nanoparticles Enhanced Dermal Regeneration in a 3-Layered Electrospun Scaffold.Adv Pharm Bull. 2024 Mar;14(1):192-207. doi: 10.34172/apb.2024.006. Epub 2023 Jul 22. Adv Pharm Bull. 2024. PMID: 38585469 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kato YP, Christiansen DL, Hahn RA, Shieh S-J, Goldstein JD, Silver FH. Mechanical Properties of collagen fibres: a comparison of reconstituted and rat tail tendon fibres. Biomaterials. 1989;10:38–42. - PubMed
-
- Zeugolis DI, Paul GR, Attenburrow G. Cross-linking of extruded collagen fibers--A biomimetic three-dimensional scaffold for tissue engineering applications. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2009;89:895–908. - PubMed
-
- Pins GD, Silver FH. A self-assembled collagen scaffold suitable for use in soft and hard tissue replacement. Materials Science and Engineering: C. 1995;3:101–7.
-
- Zeugolis DI, Paul RG, Attenburrow G. The influence of a natural cross-linking agent (Myrica rubra) on the properties of extruded collagen fibres for tissue engineering applications. Materials Science & Engineering C-Materials for Biological Applications. 2010;30:190–5.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
