GLP-1 receptor agonism ameliorates hepatic VLDL overproduction and de novo lipogenesis in insulin resistance
- PMID: 25506548
- PMCID: PMC4264039
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2014.09.005
GLP-1 receptor agonism ameliorates hepatic VLDL overproduction and de novo lipogenesis in insulin resistance
Abstract
Background/objectives: Fasting dyslipidemia is commonly observed in insulin resistant states and mechanistically linked to hepatic overproduction of very low density lipoprotein (VLDL). Recently, the incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) has been implicated in ameliorating dyslipidemia associated with insulin resistance and reducing hepatic lipid stores. Given that hepatic VLDL production is a key determinant of circulating lipid levels, we investigated the role of both peripheral and central GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonism in regulation of VLDL production.
Methods: The fructose-fed Syrian golden hamster was employed as a model of diet-induced insulin resistance and VLDL overproduction. Hamsters were treated with the GLP-1R agonist exendin-4 by intraperitoneal (ip) injection for peripheral studies or by intracerebroventricular (ICV) administration into the 3rd ventricle for central studies. Peripheral studies were repeated in vagotomised hamsters.
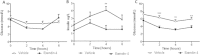
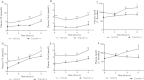
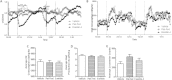
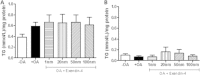
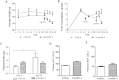
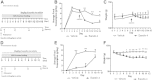
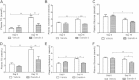
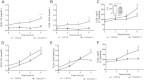
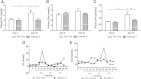
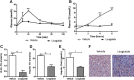
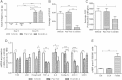
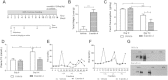
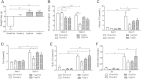
Results: Short term (7-10 day) peripheral exendin-4 enhanced satiety and also prevented fructose-induced fasting dyslipidemia and hyperinsulinemia. These changes were accompanied by decreased fasting plasma glucose levels, reduced hepatic lipid content and decreased levels of VLDL-TG and -apoB100 in plasma. The observed changes in fasting dyslipidemia could be partially explained by reduced respiratory exchange ratio (RER) thereby indicating a switch in energy utilization from carbohydrate to lipid. Additionally, exendin-4 reduced mRNA markers associated with hepatic de novo lipogenesis and inflammation. Despite these observations, GLP-1R activity could not be detected in primary hamster hepatocytes, thus leading to the investigation of a potential brain-liver axis functioning to regulate lipid metabolism. Short term (4 day) central administration of exendin-4 decreased body weight and food consumption and further prevented fructose-induced hypertriglyceridemia. Additionally, the peripheral lipid-lowering effects of exendin-4 were negated in vagotomised hamsters implicating the involvement of parasympathetic signaling.
Conclusion: Exendin-4 prevents fructose-induced dyslipidemia and hepatic VLDL overproduction in insulin resistance through an indirect mechanism involving altered energy utilization, decreased hepatic lipid synthesis and also requires an intact parasympathetic signaling pathway.
Keywords: FFA, free fatty acid; Fasting dyslipidemia; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide-1; GLP-1R, GLP-1 receptor; Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1); Hepatic steatosis; ICV, intracerebroventricular; Incretin; Insulin resistance; RER, respiratory exchange ratio; T2D, type 2 diabetes; VLDL, very low density lipoprotein; Very low density lipoprotein (VLDL); apoB100, apolipoproteinB100; ip, intraperitoneal.
Figures
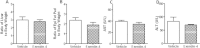

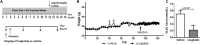
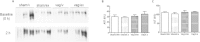
Similar articles
-
GLP-2 Dysregulates Hepatic Lipoprotein Metabolism, Inducing Fatty Liver and VLDL Overproduction in Male Hamsters and Mice.Endocrinology. 2018 Sep 1;159(9):3340-3350. doi: 10.1210/en.2018-00416. Endocrinology. 2018. PMID: 30052880
-
Inhibition of sphingolipid synthesis improves dyslipidemia in the diet-induced hamster model of insulin resistance: evidence for the role of sphingosine and sphinganine in hepatic VLDL-apoB100 overproduction.Atherosclerosis. 2013 May;228(1):98-109. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2013.01.041. Epub 2013 Feb 10. Atherosclerosis. 2013. PMID: 23466071
-
GLP-1 Elicits an Intrinsic Gut-Liver Metabolic Signal to Ameliorate Diet-Induced VLDL Overproduction and Insulin Resistance.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Dec;37(12):2252-2259. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.310251. Epub 2017 Oct 26. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 29074588
-
Influence of plasma free fatty acids on lipoprotein synthesis and diabetic dyslipidemia.Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2003 Aug;111(5):246-50. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-41284. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2003. PMID: 12951628 Review.
-
Effect of GLP-1 based therapies on diabetic dyslipidemia.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2014;10(4):238-50. doi: 10.2174/1573399810666140707092506. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2014. PMID: 24998439 Review.
Cited by
-
Nutrient infusion in the dorsal vagal complex controls hepatic lipid and glucose metabolism in rats.iScience. 2021 Mar 26;24(4):102366. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102366. eCollection 2021 Apr 23. iScience. 2021. PMID: 33870148 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin Sensitizers for Improving the Endocrine and Metabolic Profile in Overweight Women With PCOS.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Sep 1;105(9):2950-63. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa337. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32490533 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-organ Coordination of Lipoprotein Secretion by Hormones, Nutrients and Neural Networks.Endocr Rev. 2021 Nov 16;42(6):815-838. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnab008. Endocr Rev. 2021. PMID: 33743013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1 regulation of lipid and lipoprotein metabolism.Med Rev (2021). 2024 Apr 10;4(4):301-311. doi: 10.1515/mr-2024-0011. eCollection 2024 Aug. Med Rev (2021). 2024. PMID: 39135603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute Cholesterol-Lowering Effect of Exendin-4 in Ldlr-/- and C57BL/6J Mice.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2023 Jan 1;30(1):74-86. doi: 10.5551/jat.60921. Epub 2022 Mar 19. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2023. PMID: 35314564 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adeli K., Taghibiglou C., Van Iderstine S.C., Lewis G.F. Mechanisms of hepatic very low-density lipoprotein overproduction in insulin resistance. Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine. 2001;11(5):170–176. - PubMed
-
- Hein G., Baker C., Hsieh J., Farr S., Adeli K. GLP-1 and GLP-2 as yin and yang of intestinal lipoprotein production: evidence for predominance of GLP-2-stimulated postprandial lipemia in normal and insulin-resistant states. Diabetes. 2013;62(2) PMID: 23028139 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hsieh J., Longuet C., Baker C.L., Qin B., Federico L.M., Drucker D.J. The glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor is essential for postprandial lipoprotein synthesis and secretion in hamsters and mice. Diabetologia. 2010;53(3):552–561. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz E.A., Koska J., Mullin M.P., Syoufi I., Schwenke D.C., Reaven P.D. Exenatide suppresses postprandial elevations in lipids and lipoproteins in individuals with impaired glucose tolerance and recent onset type 2 diabetes mellitus. Atherosclerosis. 2010;212(1):217–222. - PubMed
-
- Farr S., Taher J., Adeli K. Glucagon-like peptide-1 as a key regulator of lipid and lipoprotein metabolism in fasting and postprandial states. Cardiovascular Hematological Disorders Drug Targets. 2014;14(2):126–136. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

