Contribution of Crk adaptor proteins to host cell and bacteria interactions
- PMID: 25506591
- PMCID: PMC4260429
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/372901
Contribution of Crk adaptor proteins to host cell and bacteria interactions
Abstract
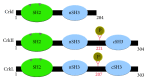
The Crk adaptor family of proteins comprises the alternatively spliced CrkI and CrkII isoforms, as well as the paralog Crk-like (CrkL) protein, which is encoded by a different gene. Initially thought to be involved in signaling during apoptosis and cell adhesion, this ubiquitously expressed family of proteins is now known to play essential roles in integrating signals from a wide range of stimuli. In this review, we describe the structure and function of the different Crk proteins. We then focus on the emerging roles of Crk adaptors during Enterobacteriaceae pathogenesis, with special emphasis on the important human pathogens Salmonella, Shigella, Yersinia, and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Throughout, we remark on opportunities for future research into this intriguing family of proteins.
Figures


References
-
- Mayer B. J., Hamaguchi M., Hanafusa H. Characterization of p47(gag-crk), a novel oncogene product with sequence similarity to a putative modulatory domain of protein-tyrosine kinases and phospholipase C. Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology. 1988;53(2):907–914. doi: 10.1101/SQB.1988.053.01.104. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ten Hoeve J., Morris C., Heisterkamp N., Groffen J. Isolation and chromosomal localization of CRKL, a human crk-like gene. Oncogene. 1993;8(9):2469–2474. - PubMed
-
- Ten Hoeve J., Arlinghaus R. B., Guo J. Q., Heisterkamp N., Groffen J. Tyrosine phosphorylation of CRKL in Philadelphia+ leukemia. Blood. 1994;84(6):1731–1736. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

