Frailty Attenuates the Impact of Metformin on Reducing Mortality in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 25506599
- PMCID: PMC4264048
Frailty Attenuates the Impact of Metformin on Reducing Mortality in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
Objective: To determine whether the protective effect of metformin against death is modified by frailty status in older adults with type 2 diabetes.
Research design and methods: We conducted a cohort study during October 1, 1999-September 30, 2006 among veterans aged 65-89 years old with type 2 diabetes but without history of liver, renal diseases, or cancers, who had sulfonylureas or metformin as the sole antidiabetic drug for ≥180 days. The Cox proportional hazard model was used to compare hazard rates of all-cause mortality between the metformin and sulfonylurea users adjusting for the propensity score of metformin use and covariates: age, race/ethnicity, diabetes duration, Charlson comorbidity score, statin use, smoking status, BMI, LDL, and HbA1c.
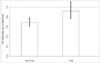
Results: In this cohort of 2,415 veterans, 307 (12.7%) were metformin users, 2,108 (87.3%) were sulfonylurea users, the mean age was 73.7±5.2 years, the mean study period was 5.6±2.3 years, the mean HbA1c at baseline was 6.7±1.0%, 23% had diabetes for ≥10 years, and 43.6% (N=1,048) died during the study period. For patients with and without frailty, the adjusted hazard ratio (HR) of death for metformin vs. sulfonylurea use were 0.92 (95% CI=0.90-1.31, p-value=0.19) and 0.69 (95% CI = 0.60-0.79, p-value<0.001), respectively. Logistic regression analyses showed that metformin (vs. sulfonylurea) was significantly associated with a decreased odds of frailty (OR: 0.66, 95% CI: 0.61-0.71, p-value <.0001).
Conclusion: Our study suggests that metformin could potentially promote longevity via preventing frailty in older adults with type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: Frailty; Metformin; Mortality; Type 2 diabetes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metformin vs sulfonylurea use and risk of dementia in US veterans aged ≥65 years with diabetes.Neurology. 2017 Oct 31;89(18):1877-1885. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000004586. Epub 2017 Sep 27. Neurology. 2017. PMID: 28954880 Free PMC article.
-
Increased cancer-related mortality for patients with type 2 diabetes who use sulfonylureas or insulin.Diabetes Care. 2006 Feb;29(2):254-8. doi: 10.2337/diacare.29.02.06.dc05-1558. Diabetes Care. 2006. PMID: 16443869
-
Risk of Incident Cancer in Veterans with Diabetes Who Use Metformin Versus Sulfonylureas.J Cancer Prev. 2024 Dec 30;29(4):140-147. doi: 10.15430/JCP.24.012. J Cancer Prev. 2024. PMID: 39790228 Free PMC article.
-
The Risk of TB in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Initiating Metformin vs Sulfonylurea Treatment.Chest. 2018 Jun;153(6):1347-1357. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2017.11.040. Epub 2017 Dec 16. Chest. 2018. PMID: 29253553
-
Race, ethnicity, and use of thiazolidinediones among US adults with diabetes.Curr Med Res Opin. 2007 Mar;23(3):489-94. doi: 10.1185/030079906X167354. Curr Med Res Opin. 2007. PMID: 17355730
Cited by
-
Frailty incidence by diabetes treatment regimens in older adults with diabetes mellitus in the ASPirin in Reducing Events in the Elderly Study.Geroscience. 2025 Jun;47(3):5169-5183. doi: 10.1007/s11357-025-01598-6. Epub 2025 Mar 17. Geroscience. 2025. PMID: 40097879 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological Systems in Promoting Frailty.Compr Physiol. 2022 Apr 26;12(3):3575-3620. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c210034. Compr Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35578945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type 2 diabetes mellitus in older adults: clinical considerations and management.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021 Sep;17(9):534-548. doi: 10.1038/s41574-021-00512-2. Epub 2021 Jun 25. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 34172940 Review.
-
Effects of early medication treatment and metformin use for cancer prevention in diabetes patients: a nationwide sample cohort study in Korea using extended landmark time analysis.Epidemiol Health. 2021;43:e2021103. doi: 10.4178/epih.e2021103. Epub 2021 Dec 17. Epidemiol Health. 2021. PMID: 34922421 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of frailty on mortality, hospitalization, cardiovascular events, and complications in patients with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024 May 28;16(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01352-6. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024. PMID: 38802895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- United States Census Bureau
-
- Gremese E, Ferraccioli G. The metabolic syndrome: the crossroads between rheumatoid arthritis and cardiovascular risk. Autoimmun Review. 2011;10:582–589. - PubMed
-
- Federal Interagency Forum on Aging-Related Statistics
-
- Pollak MN. Investigating metformin for cancer prevention and treatment: the end of the beginning. Cancer Discov. 2012;2:778–790. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical