Effectiveness of a school-based physical activity intervention on obesity in school children: a nonrandomized controlled trial
- PMID: 25510313
- PMCID: PMC4320634
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-1282
Effectiveness of a school-based physical activity intervention on obesity in school children: a nonrandomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Childhood obesity has been a serious public health problem. An effective school-based physical activity (PA) intervention is still lacking in China. This study aimed to assess the effectiveness of a school-based physical activity intervention during 12 weeks on obesity and related health outcomes in school children.
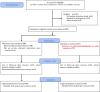
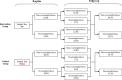
Methods: It was a non-randomized controlled trial. Altogether 921 children aged 7 to 15 years were recruited at baseline survey. Children in the intervention group (n = 388) participated in a multi-component physical activity intervention during 12 weeks that included improvement of physical education, extracurricular physical activities for overweight/obese students, physical activities at home, and health education lectures for students and parents. Children (n = 533) in the control group participated in usual practice.
Results: Participants had mean age of 10.4 years, mean body mass index (BMI) of 19.59 kg/m2, and 36.8 % of them were overweight or obese at baseline survey. The change in BMI in intervention group (-0.02 ± 0.06 kg/m2) was significantly different from that in control group (0.41 ± 0.08 kg/m2). The adjusted mean difference was -0.43 kg/m2 (95% CI: -0.63 to -0.23 kg/m2, P < 0.001). The effects on triceps, subscapular, abdominal skinfold thickness and fasting glucose were also significant in intervention group compared with control group (all P < 0.05). The change in duration of moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA) in intervention group (8.9 ± 4.3 min/day) was significantly different from that in control group (-13.8 ± 3.3 min/day). The adjusted mean difference was 22.7 min/day (95% CI: 12.2 to 33.2 min/day, P < 0.001).
Conclusions: The school-based, multi-component physical activity intervention was effective to decreasing levels of BMI, skinfold thickness, fasting glucose and increasing duration of MVPA. These findings provided evidence for the development of effective and feasible school-based obesity interventions.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov Identifier: NCT02074332 (2014-02-26).
Figures
References
-
- Ng M, Fleming T, Robinson M, Thomson B, Graetz N, Margono C, Mullany EC, Biryukov S, Abbafati C, Abera SF, Abraham JP, Abu-Rmeileh NM, Achoki T, AlBuhairan FS, Alemu ZA, Alfonso R, Ali MK, Ali R, Guzman NA, Ammar W, Anwari P, Banerjee A, Barquera S, Basu S, Bennett DA, Bhutta Z, Blore J, Cabral N, Nonato IC, Chang JC, et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2014;384(9945):766–781. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60460-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Pre-publication history
-
- The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2458/14/1282/prepub
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical