HIF-1α restricts NF-κB-dependent gene expression to control innate immunity signals
- PMID: 25510503
- PMCID: PMC4314782
- DOI: 10.1242/dmm.017285
HIF-1α restricts NF-κB-dependent gene expression to control innate immunity signals
Abstract
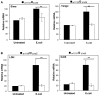
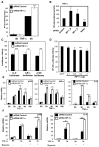
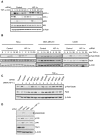
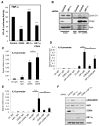
Hypoxia and inflammation are intimately linked. It is known that nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) regulates the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) system, but little is known about how HIF regulates NF-κB. Here, we show that HIF-1α represses NF-κB-dependent gene expression. HIF-1α depletion results in increased NF-κB transcriptional activity both in mammalian cells and in the model organism Drosophila melanogaster. HIF-1α depletion enhances the NF-κB response, and this required not only the TAK-IKK complex, but also CDK6. Loss of HIF-1α results in an increased angiogenic response in mammalian cancer cells and increased mortality in Drosophila following infection. These results indicate that HIF-1α is required to restrain the NF-κB response, and thus prevents excessive and damaging pro-inflammatory responses.
Keywords: Drosophila; HIF-1; Hypoxia; IKK; Inflammation; NF-κB.
© 2015. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Adli M., Baldwin A. S. (2006). IKK-i/IKKepsilon controls constitutive, cancer cell-associated NF-kappaB activity via regulation of Ser-536 p65/RelA phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 26976–26984. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht S. C., Barata A. G., Grosshans J., Teleman A. A., Dick T. P. (2011). In vivo mapping of hydrogen peroxide and oxidized glutathione reveals chemical and regional specificity of redox homeostasis. Cell Metab. 14, 819–829. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

