Effect of the starting point of half-pin insertion on the insertional torque of the pin at the tibia
- PMID: 25510759
- PMCID: PMC4276749
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.1.154
Effect of the starting point of half-pin insertion on the insertional torque of the pin at the tibia
Abstract
Purpose: The authors have observed a failure to achieve secure fixation in elderly patients when inserting a half-pin at the anteromedial surface of the tibia. The purpose of this study was to compare two methods for inserting a half-pin at tibia diaphysis in elderly patients.
Materials and methods: Twenty cadaveric tibias were divided into Group C or V. A half-pin was inserted into the tibias of Group C via the conventional method, from the anteromedial surface to the interosseous border of the tibia diaphysis, and into the tibias of Group V via the vertical method, from the anterior border to the posterior surface at the same level. The maximum insertion torque was measured during the bicortical insertion with a torque driver. The thickness of the cortex was measured by micro-computed tomography. The relationship between the thickness of the cortex engaged and the insertion torque was investigated.
Results: The maximum insertion torque and the thickness of the cortex were significantly higher in Group V than Group C. Both groups exhibited a statistically significant linear correlation between torque and thickness by Spearman's rank correlation analysis.
Conclusion: Half-pins inserted by the vertical method achieved purchase of more cortex than those inserted by the conventional method. Considering that cortical thickness and insertion torque in Group V were significantly greater than those in Group C, we suggest that the vertical method of half-pin insertion may be an alternative to the conventional method in elderly patients.
Keywords: Fracture; diaphysis; external fixation; tibia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
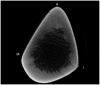



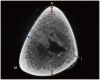
References
-
- Giannoudis PV, Schneider E. Principles of fixation of osteoporotic fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88:1272–1278. - PubMed
-
- Donaldson FE, Pankaj P, Simpson AH. Bone properties affect loosening of half-pin external fixators at the pin-bone interface. Injury. 2012;43:1764–1770. - PubMed
-
- Hyldahl C, Pearson S, Tepic S, Perren SM. Induction and prevention of pin loosening in external fixation: an in vivo study on sheep tibiae. J Orthop Trauma. 1991;5:485–492. - PubMed
-
- Donaldson FE, Pankaj P, Simpson AH. Investigation of factors affecting loosening of Ilizarov ring-wire external fixator systems at the bone-wire interface. J Orthop Res. 2012;30:726–732. - PubMed
-
- Parameswaran AD, Roberts CS, Seligson D, Voor M. Pin tract infection with contemporary external fixation: how much of a problem? J Orthop Trauma. 2003;17:503–507. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

