The p53-induced lincRNA-p21 derails somatic cell reprogramming by sustaining H3K9me3 and CpG methylation at pluripotency gene promoters
- PMID: 25512341
- PMCID: PMC4650593
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2014.165
The p53-induced lincRNA-p21 derails somatic cell reprogramming by sustaining H3K9me3 and CpG methylation at pluripotency gene promoters
Abstract
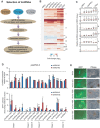
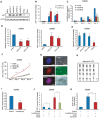
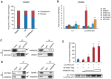
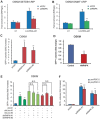
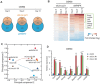
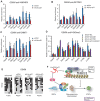
Recent studies have boosted our understanding of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in numerous biological processes, but few have examined their roles in somatic cell reprogramming. Through expression profiling and functional screening, we have identified that the large intergenic noncoding RNA p21 (lincRNA-p21) impairs reprogramming. Notably, lincRNA-p21 is induced by p53 but does not promote apoptosis or cell senescence in reprogramming. Instead, lincRNA-p21 associates with the H3K9 methyltransferase SETDB1 and the maintenance DNA methyltransferase DNMT1, which is facilitated by the RNA-binding protein HNRNPK. Consequently, lincRNA-p21 prevents reprogramming by sustaining H3K9me3 and/or CpG methylation at pluripotency gene promoters. Our results provide insight into the role of lncRNAs in reprogramming and establish a novel link between p53 and heterochromatin regulation.
Figures
References
-
- 1Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induced pluripotent stem cells in medicine and biology. Development 2013; 140:2457–2461. - PubMed
-
- 4Liu L, Xu Y, He M, et al. Transcriptional pause release is a rate-limiting step for somatic cell reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell 2014; 15:574–588. - PubMed
-
- 5Rais Y, Zviran A, Geula S, et al. Deterministic direct reprogramming of somatic cells to pluripotency. Nature 2013; 502:65–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

