Detailed mutational analysis of Vga(A) interdomain linker: implication for antibiotic resistance specificity and mechanism
- PMID: 25512423
- PMCID: PMC4335903
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.04468-14
Detailed mutational analysis of Vga(A) interdomain linker: implication for antibiotic resistance specificity and mechanism
Abstract
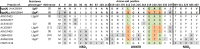
Detailed mutational analysis examines the roles of individual residues of the Vga(A) linker in determining the antibiotic resistance phenotype. It defines a narrowed region of residues 212 to 220 whose composition determines the resistance specificity to lincosamides, pleuromutilins, and/or streptogramins A. From the analogy with the recently described function of the homologous ABC-F protein EttA as a translational factor, we infer that the Vga(A) linker interacts with the ribosome and directly or indirectly affects the binding of the respective antibiotic.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Jacquet E, Girard J-MM, Ramaen O, Pamlard O, Lévaique H, Betton J-MM, Dassa E, Chesneau O, Levaique H. 2008. ATP hydrolysis and pristinamycin IIA inhibition of the Staphylococcus aureus Vga(A), a dual ABC protein involved in streptogramin A resistance. J Biol Chem 283:25332–25339. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800418200. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

