GUIDE-seq enables genome-wide profiling of off-target cleavage by CRISPR-Cas nucleases
- PMID: 25513782
- PMCID: PMC4320685
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt.3117
GUIDE-seq enables genome-wide profiling of off-target cleavage by CRISPR-Cas nucleases
Abstract
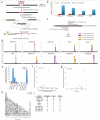
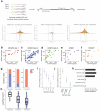
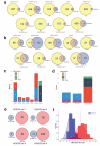
CRISPR RNA-guided nucleases (RGNs) are widely used genome-editing reagents, but methods to delineate their genome-wide, off-target cleavage activities have been lacking. Here we describe an approach for global detection of DNA double-stranded breaks (DSBs) introduced by RGNs and potentially other nucleases. This method, called genome-wide, unbiased identification of DSBs enabled by sequencing (GUIDE-seq), relies on capture of double-stranded oligodeoxynucleotides into DSBs. Application of GUIDE-seq to 13 RGNs in two human cell lines revealed wide variability in RGN off-target activities and unappreciated characteristics of off-target sequences. The majority of identified sites were not detected by existing computational methods or chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq). GUIDE-seq also identified RGN-independent genomic breakpoint 'hotspots'. Finally, GUIDE-seq revealed that truncated guide RNAs exhibit substantially reduced RGN-induced, off-target DSBs. Our experiments define the most rigorous framework for genome-wide identification of RGN off-target effects to date and provide a method for evaluating the safety of these nucleases before clinical use.
Figures



Comment in
-
Mapping the precision of genome editing.Nat Biotechnol. 2015 Feb;33(2):150-2. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3142. Nat Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25658281 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

