Evolution of the syphilis epidemic among men who have sex with men
- PMID: 25514173
- PMCID: PMC4470884
- DOI: 10.1071/SH14173
Evolution of the syphilis epidemic among men who have sex with men
Abstract
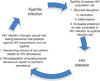
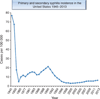
Syphilis has existed for millenni, but its epidemiology was only recently linked to men who have sex with men (MSM) after the introduction of penicillin in the 1940s; the syphilis epidemic became concentrated within the MSM community in subsequent decades. The HIV/AIDS epidemic in the 1980s led to a surge of new syphilis cases and revealed the potentiation between HIV and syphilis, as evidenced by a shift in the natural history of neurosyphilis. In response, MSM revolutionised their sexual behaviour by implementing community-driven seroadaptive strategies to stem HIV transmission. The Centers for Disease Control in the US called for the elimination of syphilis in the late 1990s since the rates had fallen sharply but this effort was overtaken by a resurgence of global outbreaks among MSM in the 2000s, many of which were linked to methamphetamine use and sexual networking websites. Syphilis remains highly prevalent today, especially among MSM and individuals infected with HIV, and it continues to present a significant public health conundrum. Innovative syphilis prevention strategies are warranted. MSM engaging in high-risk behaviour such as condomless anal receptive intercourse, sex with multiple partners or recreational drug use should be routinely screened for syphilis infection; they should also be counselled about the limits of seroadaptive behaviours and HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis as they relate to syphilis transmission.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Mahoney JF, Arnold RC, Sterner BL, Harris A, Zwally MR. Penicillin treatment of early syphilis: II. JAMA. 1984;251:2005–2010. - PubMed
-
- Parran T. Shadow on the land. New York: Reynal and Hitchcock; 1937.
-
- Holmes KK. Azithromycin versus penicillin G benzathine for early syphilis. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1291–1293. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

