The shared crosstalk of multiple pathways involved in the inflammation between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary artery disease based on a digital gene expression profile
- PMID: 25514790
- PMCID: PMC4267808
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113659
The shared crosstalk of multiple pathways involved in the inflammation between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary artery disease based on a digital gene expression profile
Abstract
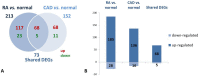
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and coronary artery disease (CAD) are both complex inflammatory diseases, and an increased prevalence of CAD and a high rate of mortality have been observed in RA patients. But the molecular mechanism of inflammation that is shared between the two disorders is unclear. High-throughput techniques, such as transcriptome analysis, are becoming important tools for genetic biomarker discovery in highly complex biological samples, which is critical for the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of disease. In the present study, we reported one type of transcriptome analysis method: digital gene expression profiling of peripheral blood mononuclear cells of 10 RA patients, 10 CAD patients and 10 healthy people. In all, 213 and 152 differently expressed genes (DEGs) were identified in RA patients compared with normal controls (RA vs. normal) and CAD patients compared with normal controls (CAD vs. normal), respectively, with 73 shared DEGs between them. Using this technique in combination with Ingenuity Pathways Analysis software, the effects on inflammation of four shared canonical pathways, three shared activated predicted upstream regulators and three shared molecular interaction networks were identified and explored. These shared molecular mechanisms may provide the genetic basis and potential targets for optimizing the application of current drugs to more effectively treat these diseases simultaneously and for preventing one when the other is diagnosed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Lee DM, Weinblatt ME (2001) Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 358:903–911. - PubMed
-
- Kriszbacher I, Koppan M, Bodis J (2005) Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 353: 429–430; author reply 429–430. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez-Gay MA, Gonzalez-Juanatey C, Martin J (2005) Rheumatoid arthritis: a disease associated with accelerated atherogenesis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 35:8–17. - PubMed
-
- Solomon DH, Karlson EW, Rimm EB, Cannuscio CC, Mandl LA, et al. (2003) Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in women diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis. Circulation 107:1303–1307. - PubMed
-
- Dessein PH, Joffe BI, Veller MG, Stevens BA, Tobias M, et al. (2005) Traditional and nontraditional cardiovascular risk factors are associated with atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 32:435–442. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

