Determining the quality and complexity of next-generation sequencing data without a reference genome
- PMID: 25514851
- PMCID: PMC4298064
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-014-0555-3
Determining the quality and complexity of next-generation sequencing data without a reference genome
Abstract
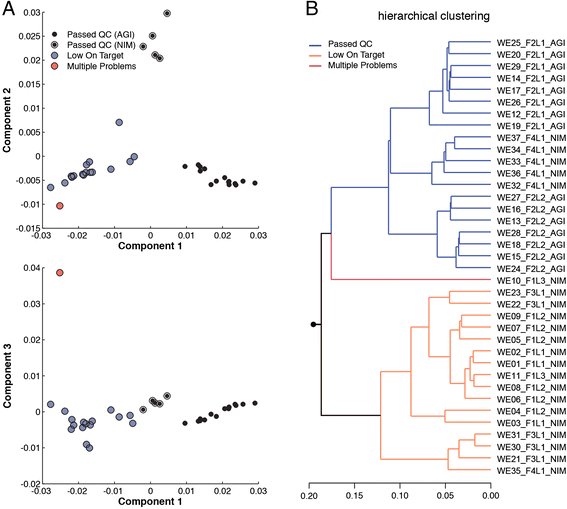
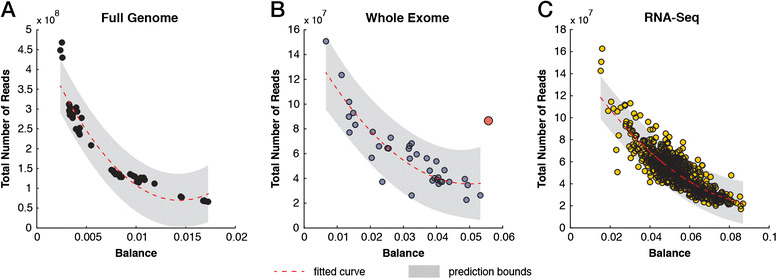
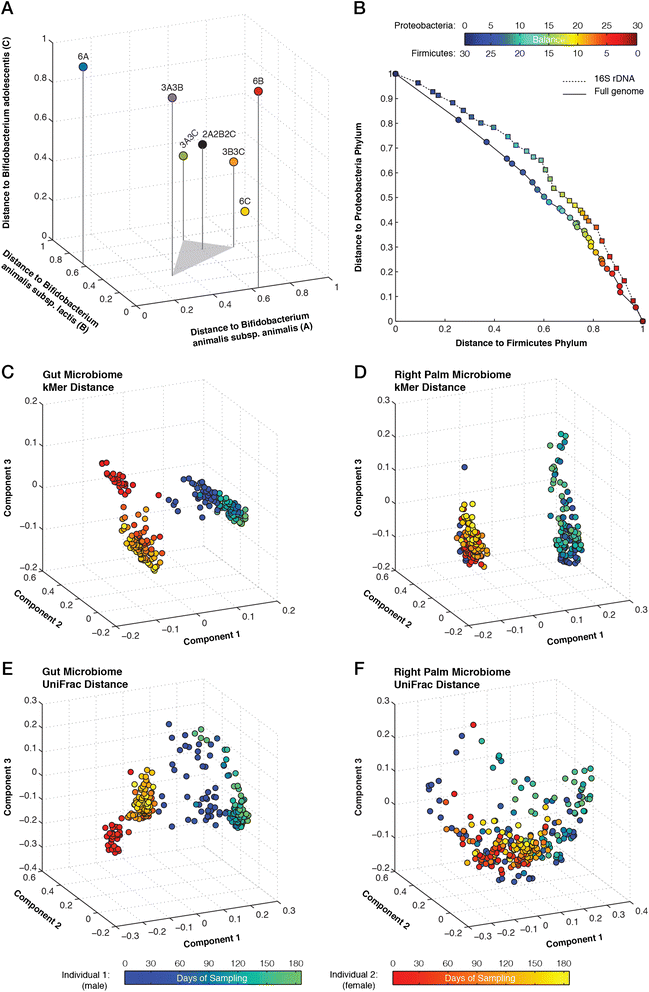
We describe an open-source kPAL package that facilitates an alignment-free assessment of the quality and comparability of sequencing datasets by analyzing k-mer frequencies. We show that kPAL can detect technical artefacts such as high duplication rates, library chimeras, contamination and differences in library preparation protocols. kPAL also successfully captures the complexity and diversity of microbiomes and provides a powerful means to study changes in microbial communities. Together, these features make kPAL an attractive and broadly applicable tool to determine the quality and comparability of sequence libraries even in the absence of a reference sequence. kPAL is freely available at https://github.com/LUMC/kPAL webcite.
Figures



References
-
- Costello M, Pugh TJ, Fennell TJ, Stewart C, Lichtenstein L, Meldrim JC, Fostel JL, Friedrich DC, Perrin D, Dionne D, Kim S, Gabriel SB, Lander ES, Fisher S, Getz G. Discovery and characterization of artifactual mutations in deep coverage targeted capture sequencing data due to oxidative DNA damage during sample preparation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:e67. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1443. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kidd JM, Sampas N, Antonacci F, Graves T, Fulton R, Hayden HS, Alkan C, Malig M, Ventura M, Giannuzzi G, Kallicki J, Anderson P, Tsalenko A, Yamada NA, Tsang P, Kaul R, Wilson RK, Bruhn L, Eichler EE. Characterization of missing human genome sequences and copy-number polymorphic insertions. Nat Methods. 2010;7:365–371. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1451. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

