The cognitive defects of neonatally irradiated mice are accompanied by changed synaptic plasticity, adult neurogenesis and neuroinflammation
- PMID: 25515237
- PMCID: PMC4280038
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-1326-9-57
The cognitive defects of neonatally irradiated mice are accompanied by changed synaptic plasticity, adult neurogenesis and neuroinflammation
Abstract
Background/purpose of the study: Epidemiological evidence suggests that low doses of ionising radiation (≤1.0 Gy) produce persistent alterations in cognition if the exposure occurs at a young age. The mechanisms underlying such alterations are unknown. We investigated the long-term effects of low doses of total body gamma radiation on neonatally exposed NMRI mice on the molecular and cellular level to elucidate neurodegeneration.
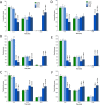
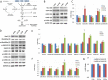
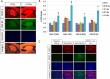
Results: Significant alterations in spontaneous behaviour were observed at 2 and 4 months following a single 0.5 or 1.0 Gy exposure. Alterations in the brain proteome, transcriptome, and several miRNAs were analysed 6-7 months post-irradiation in the hippocampus, dentate gyrus (DG) and cortex. Signalling pathways related to synaptic actin remodelling such as the Rac1-Cofilin pathway were altered in the cortex and hippocampus. Further, synaptic proteins MAP-2 and PSD-95 were increased in the DG and hippocampus (1.0 Gy). The expression of synaptic plasticity genes Arc, c-Fos and CREB was persistently reduced at 1.0 Gy in the hippocampus and cortex. These changes were coupled to epigenetic modulation via increased levels of microRNAs (miR-132/miR-212, miR-134). Astrogliosis, activation of insulin-growth factor/insulin signalling and increased level of microglial cytokine TNFα indicated radiation-induced neuroinflammation. In addition, adult neurogenesis within the DG was persistently negatively affected after irradiation, particularly at 1.0 Gy.
Conclusion: These data suggest that neurocognitive disorders may be induced in adults when exposed at a young age to low and moderate cranial doses of radiation. This raises concerns about radiation safety standards and regulatory practices.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Ionising radiation immediately impairs synaptic plasticity-associated cytoskeletal signalling pathways in HT22 cells and in mouse brain: an in vitro/in vivo comparison study.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 20;9(10):e110464. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110464. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25329592 Free PMC article.
-
Out-of-Field Hippocampus from Partial-Body Irradiated Mice Displays Changes in Multi-Omics Profile and Defects in Neurogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 20;22(8):4290. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084290. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33924260 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal Irradiation Leads to Persistent Proteome Alterations Involved in Synaptic Plasticity in the Mouse Hippocampus and Cortex.J Proteome Res. 2015 Nov 6;14(11):4674-86. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b00564. Epub 2015 Oct 12. J Proteome Res. 2015. PMID: 26420666
-
Hippocampal dysfunctions caused by cranial irradiation: a review of the experimental evidence.Brain Behav Immun. 2015 Mar;45:287-96. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2015.01.007. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Brain Behav Immun. 2015. PMID: 25596174 Review.
-
Postnatal irradiation-induced hippocampal neuropathology, cognitive impairment and aging.Brain Dev. 2017 Apr;39(4):277-293. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2016.11.001. Epub 2016 Nov 19. Brain Dev. 2017. PMID: 27876394 Review.
Cited by
-
In-Utero Low-Dose Irradiation Leads to Persistent Alterations in the Mouse Heart Proteome.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 8;11(6):e0156952. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156952. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27276052 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative proteomic analysis reveals AK2 as potential biomarker for late normal tissue radiotoxicity.Radiat Oncol. 2019 Aug 9;14(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s13014-019-1351-8. Radiat Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31399108 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the study of the molecular biological mechanisms of radiation-induced brain injury.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Aug 15;13(8):3275-3299. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37693137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Infusion of etoposide in the CA1 disrupts hippocampal immediate early gene expression and hippocampus-dependent learning.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 27;12(1):12834. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17052-y. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35896679 Free PMC article.
-
Stochastic Modeling of Radiation-induced Dendritic Damage on in silico Mouse Hippocampal Neurons.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 3;8(1):5494. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23855-9. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29615729 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ron E, Modan B, Floro S, Harkedar I, Gurewitz R. Mental function following scalp irradiation during childhood. Am J Epidemiol. 1982;116:149–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

