The extracellular N-terminal domain of G-protein coupled receptor 83 regulates signaling properties and is an intramolecular inverse agonist
- PMID: 25516095
- PMCID: PMC4300838
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-0500-7-913
The extracellular N-terminal domain of G-protein coupled receptor 83 regulates signaling properties and is an intramolecular inverse agonist
Abstract
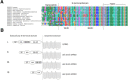
Background: Recently, the orphan G-protein coupled receptor 83 (GPR83) was identified as a new participant in body weight regulation. This receptor is highly expressed in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus and is regulated in response to nutrient availability. Gpr83 knock-out mice are protected from diet-induced obesity. Moreover, in a previous study, we designed and characterized several artificial constitutively activating mutations (CAMs) in GPR83. A particular CAM was located in the extracellular N-terminal domain (eNDo) that is highly conserved among GPR83 orthologs. This suggests the contribution of this receptor part into regulation of signaling, which needed a more detailed investigation.
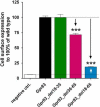
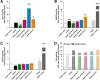
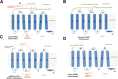
Findings: In this present study, therefore, we further explored the role of the eNDo in regulating GPR83-signaling and demonstrate a proof-of-principle approach in that deletion mutants are characterized by a strong increase in basal Gq/11-mediated signaling, whilst none of the additionally characterized signaling pathways (Gs, Gi, G12/13) were activated by the N-terminal deletion variants. Of note, we detected basal GPR83 MAPK-activity of the wild type receptor, which was not increased in the deletion variants.
Conclusions: Finally, the extracellular portion of GPR83 has a strong regulatory function on this receptor. A suppressive - inverse agonistic - effect of the eNDo on GPR83 signaling activity is demonstrated here, which also suggests a putative link between extracellular receptor activation and proteolytic cleavage. These new insights highlight important aspects of GPR83-regulation and might open options in the development of tools to modulate GPR83-signaling.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

