Upper-gastrointestinal bleeding secondary to peptic ulcer disease: incidence and outcomes
- PMID: 25516672
- PMCID: PMC4265619
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17568
Upper-gastrointestinal bleeding secondary to peptic ulcer disease: incidence and outcomes
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the incidence, surgery, mortality, and readmission of upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB) secondary to peptic ulcer disease (PUD).
Methods: Administrative databases identified all hospitalizations for UGIB secondary to PUD in Alberta, Canada from 2004 to 2010 (n = 7079) using the International Classification of Diseases Codes (ICD-10). A subset of the data was validated using endoscopy reports. Positive predictive value and sensitivity with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated. Incidence of UGIB secondary to PUD was calculated. Logistic regression was used to evaluate surgery, in-hospital mortality, and 30-d readmission to hospital with recurrent UGIB secondary to PUD. Co-variants accounted for in our logistic regression model included: age, sex, area of residence (i.e., urban vs rural), number of Charlson comorbidities, presence of perforated PUD, undergoing upper endoscopy, year of admission, and interventional radiological attempt at controlling bleeding. A subgroup analysis (n = 6356) compared outcomes of patients with gastric ulcers to those with duodenal ulcers. Adjusted estimates are presented as odds ratios (OR) with 95%CI.
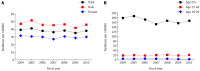
Results: The positive predictive value and sensitivity of ICD-10 coding for UGIB secondary to PUD were 85.2% (95%CI: 80.2%-90.2%) and 77.1% (95%CI: 69.1%-85.2%), respectively. The annual incidence between 2004 and 2010 ranged from 35.4 to 41.2 per 100000. Overall risk of surgery, in-hospital mortality, and 30-d readmission to hospital for UGIB secondary to PUD were 4.3%, 8.5%, and 4.7%, respectively. Interventional radiology to control bleeding was performed in 0.6% of patients and 76% of these patients avoided surgical intervention. Thirty-day readmission significantly increased from 3.1% in 2004 to 5.2% in 2010 (OR = 1.07; 95%CI: 1.01-1.14). Rural residents (OR rural vs urban: 2.35; 95%CI: 1.83-3.01) and older individuals (OR ≥ 65 vs < 65: 1.57; 95%CI: 1.21-2.04) were at higher odds of being readmitted to hospital. Patients with duodenal ulcers had higher odds of dying (OR = 1.27; 95%CI: 1.05-1.53), requiring surgery (OR = 1.73; 95%CI: 1.34-2.23), and being readmitted to hospital (OR = 1.54; 95%CI: 1.19-1.99) when compared to gastric ulcers.
Conclusion: UGIB secondary to PUD, particularly duodenal ulcers, was associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Early readmissions increased over time and occurred more commonly in rural areas.
Keywords: Digestive system surgical procedures; Endoscopy; Epidemiology; Incidence; Mortality; Peptic ulcer hemorrhage; Validation studies.
Figures

References
-
- Sung JJ. Marshall and Warren Lecture 2009: peptic ulcer bleeding: an expedition of 20 years from 1989-2009. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;25:229–233. - PubMed
-
- Lau JY, Barkun A, Fan DM, Kuipers EJ, Yang YS, Chan FK. Challenges in the management of acute peptic ulcer bleeding. Lancet. 2013;381:2033–2043. - PubMed
-
- Hearnshaw SA, Logan RF, Lowe D, Travis SP, Murphy MF, Palmer KR. Acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding in the UK: patient characteristics, diagnoses and outcomes in the 2007 UK audit. Gut. 2011;60:1327–1335. - PubMed
-
- Khamaysi I, Gralnek IM. Acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB) - initial evaluation and management. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2013;27:633–638. - PubMed
-
- Sung JJ, Kuipers EJ, El-Serag HB. Systematic review: the global incidence and prevalence of peptic ulcer disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2009;29:938–946. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

