Helicobacter pylori infection and atopic diseases: is there a relationship? A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 25516679
- PMCID: PMC4265626
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17635
Helicobacter pylori infection and atopic diseases: is there a relationship? A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Aim: To review and conduct a meta-analysis of the existing literature on the relationship between Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), atopy and allergic diseases.
Methods: Studies published in English assessing the prevalence of atopy and/or allergic diseases in patients with H. pylori infection and the prevalence of H. pylori infection in patients with atopy and/or allergic diseases were identified through a MEDLINE search (1950-2014). Random-effect model was used for the meta-analysis.
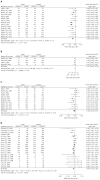
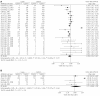
Results: Pooled results of case-control studies showed a significant inverse association of H. pylori infection with atopy/allergic disease or with exclusively atopy, but not with allergic disease, whereas pooled results of cross-sectional studies showed only a significant association between allergic disease and H. pylori infection.
Conclusion: There is some evidence of an inverse association between atopy/allergic diseases and H. pylori infection, although further studied are needed.
Keywords: Allergic diseases; Atopy; Helicobacter pylori; Hygiene hypothesis; Infection.
Figures
References
-
- Mallol J, Crane J, von Mutius E, Odhiambo J, Keil U, Stewart A. The International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) Phase Three: a global synthesis. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr) 2013;41:73–85. - PubMed
-
- Rigoli L, Briuglia S, Caimmi S, Ferraú V, Gallizzi R, Leonardi S, La Rosa M, Salpietro C. Gene-environment interaction in childhood asthma. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2011;24:41–47. - PubMed
-
- Marshall GD. Internal and external environmental influences in allergic diseases. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2004;104:S1–S6. - PubMed
-
- Nicolaou N, Siddique N, Custovic A. Allergic disease in urban and rural populations: increasing prevalence with increasing urbanization. Allergy. 2005;60:1357–1360. - PubMed
-
- WHO European Centre for Environment and Health. Effects of air pollution on children’s health and development - a review of the evidence. Copenhagen, WHO Regional Office for Europe, 200. Accessed 6 March, 2007. Available from: http://www.euro.who.int/document/E86575.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

