Clinical outcomes after parathyroidectomy in a nationwide cohort of patients on hemodialysis
- PMID: 25516915
- PMCID: PMC4284409
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.03520414
Clinical outcomes after parathyroidectomy in a nationwide cohort of patients on hemodialysis
Abstract
Background and objectives: Patients receiving dialysis undergo parathyroidectomy to improve laboratory parameters in resistant hyperparathyroidism with the assumption that clinical outcomes will also improve. However, no randomized clinical trial data demonstrate the benefits of parathyroidectomy. This study aimed to evaluate clinical outcomes up to 1 year after parathyroidectomy in a nationwide sample of patients receiving hemodialysis.
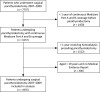
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Using data from the US Renal Data System, this study identified prevalent hemodialysis patients aged ≥18 years with Medicare as primary payers who underwent parathyroidectomy from 2007 to 2009. Baseline characteristics and comorbid conditions were assessed in the year preceding parathyroidectomy; clinical events were identified in the year preceding and the year after parathyroidectomy. After parathyroidectomy, patients were censored at death, loss of Medicare coverage, kidney transplant, change in dialysis modality, or 365 days. This study estimated cause-specific event rates for both periods and rate ratios comparing event rates in the postparathyroidectomy versus preparathyroidectomy periods.
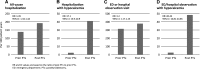
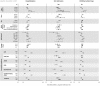
Results: Of 4435 patients who underwent parathyroidectomy, 2.0% died during the parathyroidectomy hospitalization and the 30 days after discharge. During the 30 days after discharge, 23.8% of patients were rehospitalized; 29.3% of these patients required intensive care. In the year after parathyroidectomy, hospitalizations were higher by 39%, hospital days by 58%, intensive care unit admissions by 69%, and emergency room/observation visits requiring hypocalcemia treatment by 20-fold compared with the preceding year. Cause-specific hospitalizations were higher for acute myocardial infarction (rate ratio, 1.98; 95% confidence interval, 1.60 to 2.46) and dysrhythmia (rate ratio 1.4; 95% confidence interval1.16 to 1.78); fracture rates did not differ (rate ratio 0.82; 95% confidence interval 0.6 to 1.1).
Conclusions: Parathyroidectomy is associated with significant morbidity in the 30 days after hospital discharge and in the year after the procedure. Awareness of clinical events will assist in developing evidence-based risk/benefit determinations for the indication for parathyroidectomy.
Keywords: hemodialysis; hyperparathyroidism; mortality.
Copyright © 2015 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Dysphoria induced in dialysis providers by secondary hyperparathyroidism.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015 Jan 7;10(1):9-11. doi: 10.2215/CJN.11551114. Epub 2014 Dec 16. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25516914 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Tentori F, Blayney MJ, Albert JM, Gillespie BW, Kerr PG, Bommer J, Young EW, Akizawa T, Akiba T, Pisoni RL, Robinson BM, Port FK: Mortality risk for dialysis patients with different levels of serum calcium, phosphorus, and PTH: The Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS). Am J Kidney Dis 52: 519–530, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Gupta PK, Smith RB, Gupta H, Forse RA, Fang X, Lydiatt WM: Outcomes after thyroidectomy and parathyroidectomy. Head Neck 34: 477–484, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD-MBD Work Group : KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis, evaluation, prevention, and treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD). Kidney Int Suppl 113: S1–S130, 2009 - PubMed
-
- National Kidney Foundation : K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for bone metabolism and disease in chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis 42[Suppl 3]: S1–S201, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Kestenbaum B, Andress DL, Schwartz SM, Gillen DL, Seliger SL, Jadav PR, Sherrard DJ, Stehman-Breen C: Survival following parathyroidectomy among United States dialysis patients. Kidney Int 66: 2010–2016, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

