Structure of the rabbit ryanodine receptor RyR1 at near-atomic resolution
- PMID: 25517095
- PMCID: PMC4338550
- DOI: 10.1038/nature14063
Structure of the rabbit ryanodine receptor RyR1 at near-atomic resolution
Abstract
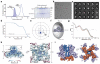
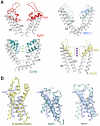
The ryanodine receptors (RyRs) are high-conductance intracellular Ca(2+) channels that play a pivotal role in the excitation-contraction coupling of skeletal and cardiac muscles. RyRs are the largest known ion channels, with a homotetrameric organization and approximately 5,000 residues in each protomer. Here we report the structure of the rabbit RyR1 in complex with its modulator FKBP12 at an overall resolution of 3.8 Å, determined by single-particle electron cryomicroscopy. Three previously uncharacterized domains, named central, handle and helical domains, display the armadillo repeat fold. These domains, together with the amino-terminal domain, constitute a network of superhelical scaffold for binding and propagation of conformational changes. The channel domain exhibits the voltage-gated ion channel superfamily fold with distinct features. A negative-charge-enriched hairpin loop connecting S5 and the pore helix is positioned above the entrance to the selectivity-filter vestibule. The four elongated S6 segments form a right-handed helical bundle that closes the pore at the cytoplasmic border of the membrane. Allosteric regulation of the pore by the cytoplasmic domains is mediated through extensive interactions between the central domains and the channel domain. These structural features explain high ion conductance by RyRs and the long-range allosteric regulation of channel activities.
Figures











References
-
- Pessah IN, Waterhouse AL, Casida JE. The calcium-ryanodine receptor complex of skeletal and cardiac muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985;128:449–56. - PubMed
-
- Inui M, Saito A, Fleischer S. Purification of the ryanodine receptor and identity with feet structures of junctional terminal cisternae of sarcoplasmic reticulum from fast skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:1740–7. - PubMed
-
- Lai FA, Erickson HP, Rousseau E, Liu QY, Meissner G. Purification and reconstitution of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1988;331:315–9. - PubMed
-
- Takeshima H, et al. Primary structure and expression from complementary DNA of skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor. Nature. 1989;339:439–45. - PubMed
-
- Rossi D, Sorrentino V. Molecular genetics of ryanodine receptors Ca2+-release channels. Cell Calcium. 2002;32:307–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

